Solar Energy Systems Interact with Smart Grid Technologies
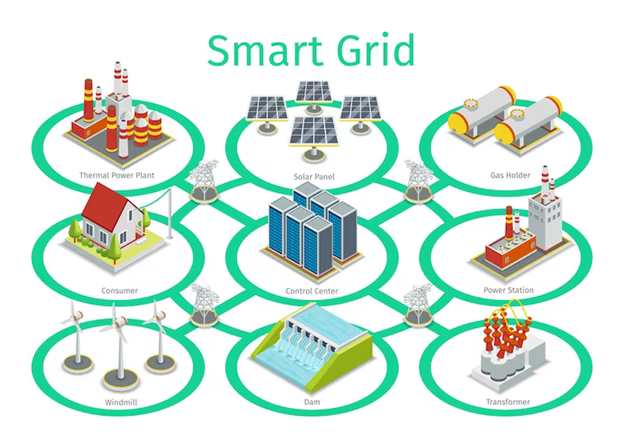
Solar energy systems interact with smart grid technologies through a variety of mechanisms and applications that optimize energy generation, distribution, consumption, and grid management. Smart grid technologies enable seamless integration of solar power into the electricity grid, improve grid reliability, efficiency, and resilience, and facilitate dynamic interactions between grid operators, energy providers, and energy consumers. Here are some key ways in which solar energy systems interact with smart grid technologies:
Grid Integration and Control: Smart grid technologies enable the integration of solar energy systems, such as rooftop solar panels, solar farms, and solar microgrids, into the electricity grid through advanced grid control and management systems. Grid-connected solar inverters, distributed energy resources (DER) management systems, and grid automation technologies facilitate real-time monitoring, control, and coordination of solar power injection, voltage regulation, and frequency response, ensuring grid stability and reliability.
Demand Response and Load Flexibility: Solar energy systems support demand response programs and load flexibility initiatives by adjusting energy production and consumption in response to grid conditions, market signals, and customer preferences. Smart grid-enabled demand response platforms, smart meters, and energy management systems enable solar customers to participate in demand-side management programs, curtail energy usage during peak periods, and optimize self-consumption of solar power, reducing electricity costs and grid congestion.
Energy Storage Integration: Solar energy systems integrate with energy storage technologies, such as batteries, pumped hydro storage, and thermal storage, to store excess solar energy and discharge it when needed, enhancing grid flexibility, reliability, and resilience. Smart grid-enabled energy storage systems, combined with solar PV, provide grid services such as peak shaving, load shifting, frequency regulation, and backup power, optimizing renewable energy integration and supporting grid stability during intermittent solar generation.
Predictive Analytics and Forecasting: Smart grid technologies utilize predictive analytics, machine learning algorithms, and weather forecasting models to forecast solar energy generation, grid demand, and market conditions with high accuracy. Solar power forecasting enables grid operators, energy providers, and market participants to anticipate solar output variability, optimize grid operations, and balance supply and demand in real-time, ensuring grid reliability and efficient resource allocation.
Grid-Interactive Solar Inverters: Grid-interactive solar inverters enable bidirectional power flow, voltage regulation, and reactive power control, allowing solar energy systems to dynamically respond to grid signals and voltage fluctuations. Smart inverters, such as advanced inverter functions (AIF) and volt-var control (VVC), support grid stability, power quality, and fault ride-through capabilities, enhancing grid resilience and accommodating higher levels of solar penetration.
Peer-to-Peer Energy Trading: Solar energy systems participate in peer-to-peer energy trading platforms and transactive energy markets, enabling prosumers to buy, sell, and exchange solar-generated electricity directly with neighboring consumers, businesses, or grid operators. Blockchain technology, decentralized energy platforms, and smart contracts facilitate secure, transparent, and automated energy transactions, empowering solar owners to monetize excess generation, optimize self-consumption, and foster community-based energy sharing initiatives.
Grid Resilience and Microgrid Integration: Solar energy systems support grid resilience and microgrid integration by providing distributed generation, backup power, and islanding capabilities during grid outages or emergencies. Smart microgrid controllers, autonomous operation algorithms, and islanding detection systems enable solar-powered microgrids to disconnect from the main grid, operate independently, and maintain critical loads during blackouts, enhancing community resilience and emergency preparedness.
Overall, the interaction between solar energy systems and smart grid technologies enables a more flexible, efficient, and responsive electricity grid, capable of accommodating high levels of renewable energy penetration, optimizing energy resources, and empowering consumers to actively participate in the energy transition. By leveraging smart grid solutions, solar energy contributes to a more sustainable, resilient, and intelligent energy ecosystem that supports the integration of renewable energy sources, fosters grid modernization, and enables a transition to a low-carbon energy future.
Thank you,
