Snapshot Work
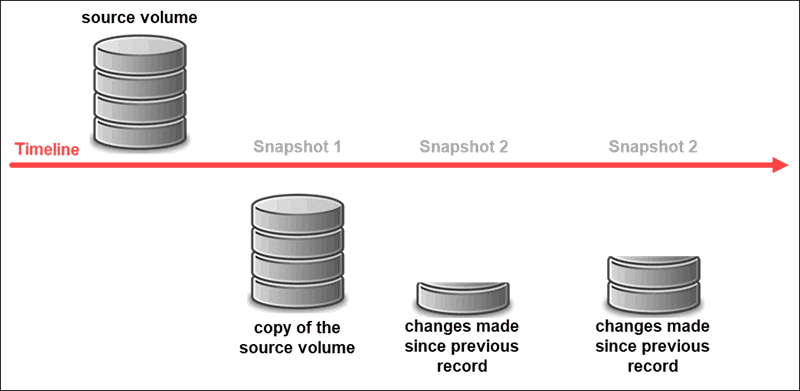
The process of how snapshots work in virtualization involves several steps. Here's a detailed explanation of how snapshots function in a typical virtualization environment:
-
Snapshot Creation:
- When a user initiates the creation of a snapshot for a virtual machine (VM), the virtualization platform takes a point-in-time snapshot of the VM's state. This includes capturing the current contents of the VM's virtual disks, as well as the state of its memory (RAM) at that moment.
-
Differential Disk Creation:
- After the snapshot is created, the virtualization platform typically creates a differential disk, also known as a snapshot disk or delta disk. The differential disk stores any changes made to the VM's virtual disks since the snapshot was taken. Initially, the differential disk is empty, as it only contains changes made after the snapshot was created.
-
Redirected Write Operations:
- With the snapshot in place, any write operations performed on the VM are redirected to the differential disk instead of modifying the original virtual disks directly. This ensures that the original virtual disks remain unchanged, while new writes are captured in the differential disk.
-
Read Operations:
- Read operations continue to be serviced from the original virtual disks. Since the snapshot preserves the state of the VM at the time it was taken, read operations access the VM's virtual disks as they existed at that point in time.
-
Snapshot Usage:
- Users can continue to use the VM normally after the snapshot is created. They can make changes, install software, or perform other operations. The snapshot provides a point-in-time reference that can be used to revert the VM to its original state if needed.
-
Reverting to Snapshot:
- If users decide to revert the VM to the state captured by the snapshot, the virtualization platform discards any changes stored in the differential disk and reverts the VM to its original state. This effectively rolls back the VM's virtual disks and memory to the state captured by the snapshot.
-
Snapshot Deletion:
- Users can also choose to delete a snapshot when it is no longer needed. When a snapshot is deleted, any changes stored in the differential disk are consolidated back into the original virtual disks, and the differential disk is removed. This process frees up storage space and removes the snapshot from the VM.
Overall, snapshots provide a powerful mechanism for capturing and preserving the state of virtual machines in virtualization environments. They enable users to revert to previous states, recover from errors, and perform backup and recovery operations efficiently. However, it's important to manage snapshots properly to avoid performance degradation and storage issues.
Thank you,
