Advanced Encryption Standard (AES)
AES, which stands for Advanced Encryption Standard, is a symmetric key block cipher that has become the de facto standard for encrypting electronic data. It was established by the U.S. National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) in 2001 to replace the aging Data Encryption Standard (DES) and Triple-DES (3DES) algorithms. AES is widely used in various applications, including securing communications, data storage, and encryption in hardware and software systems.
Key features of AES include:
-
Symmetric Key Algorithm:
- Like DES, AES is a symmetric key algorithm, meaning the same secret key is used for both encryption and decryption of the data.
-
Block Cipher:
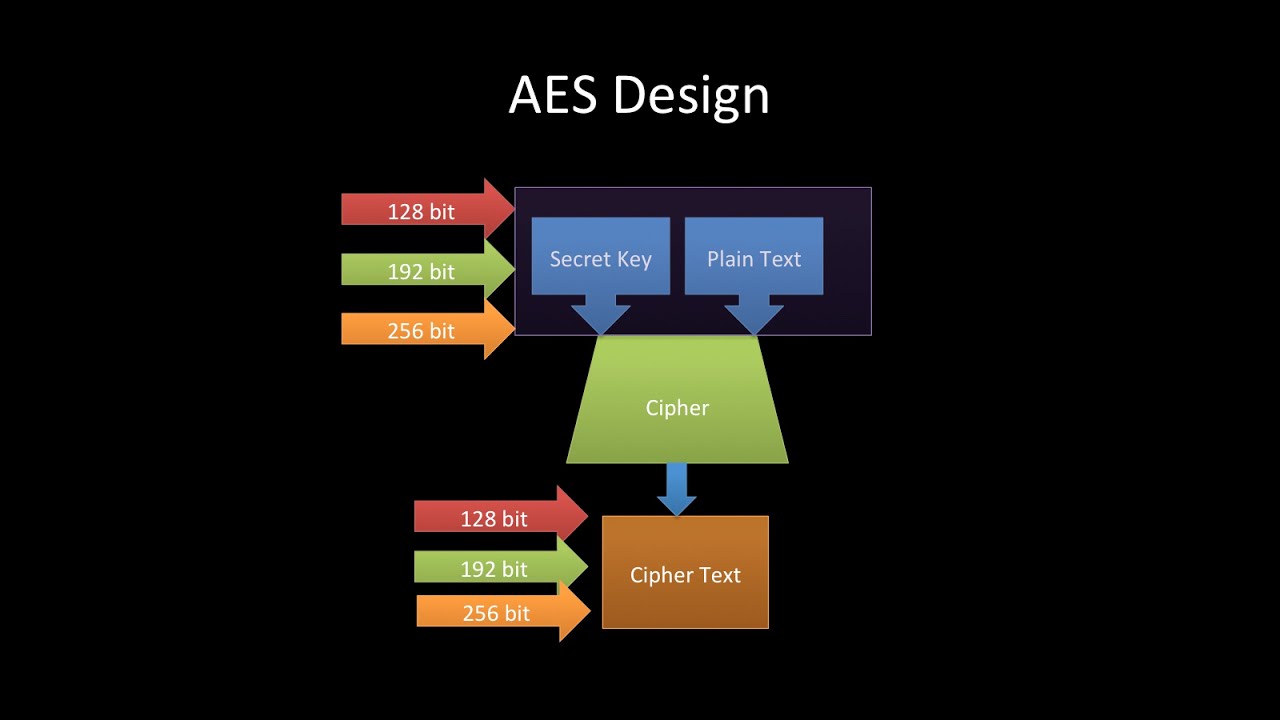
- AES operates on fixed-size blocks of data, with a block size of 128 bits. It encrypts and decrypts data in blocks rather than processing the entire message as a single unit.
-
Key Lengths:
- AES supports three different key lengths: 128 bits, 192 bits, and 256 bits. The longer the key length, the stronger the encryption, as it increases the difficulty of brute-force attacks.
-
Rounds:
- AES operates through multiple rounds of processing, with the number of rounds depending on the key length. For AES with a 128-bit key, there are 10 rounds; for 192-bit key, there are 12 rounds; and for 256-bit key, there are 14 rounds.
-
Substitution-Permutation Network:
- AES uses a substitution-permutation network (SPN) structure, which involves multiple rounds of substitution and permutation operations applied to the data and the key.
-
Security:
- AES has undergone extensive analysis by cryptographers worldwide and is considered secure against all known cryptographic attacks when implemented correctly with sufficiently long keys.
-
Efficiency:
- AES is computationally efficient and well-suited for implementation in both software and hardware. Its simplicity and speed make it suitable for a wide range of applications, including embedded systems and resource-constrained environments.
-
Wide Adoption:
- AES has been adopted by governments, organizations, and industries worldwide as the standard encryption algorithm for securing sensitive data. It is used in protocols like TLS/SSL for secure web browsing, as well as in encryption software and hardware.
Overall, AES represents a significant advancement in encryption technology, providing strong security, efficiency, and versatility for protecting digital data in various contexts. Its widespread adoption and rigorous cryptographic analysis have established it as a trusted standard for encryption.
Thank you,
