Valency
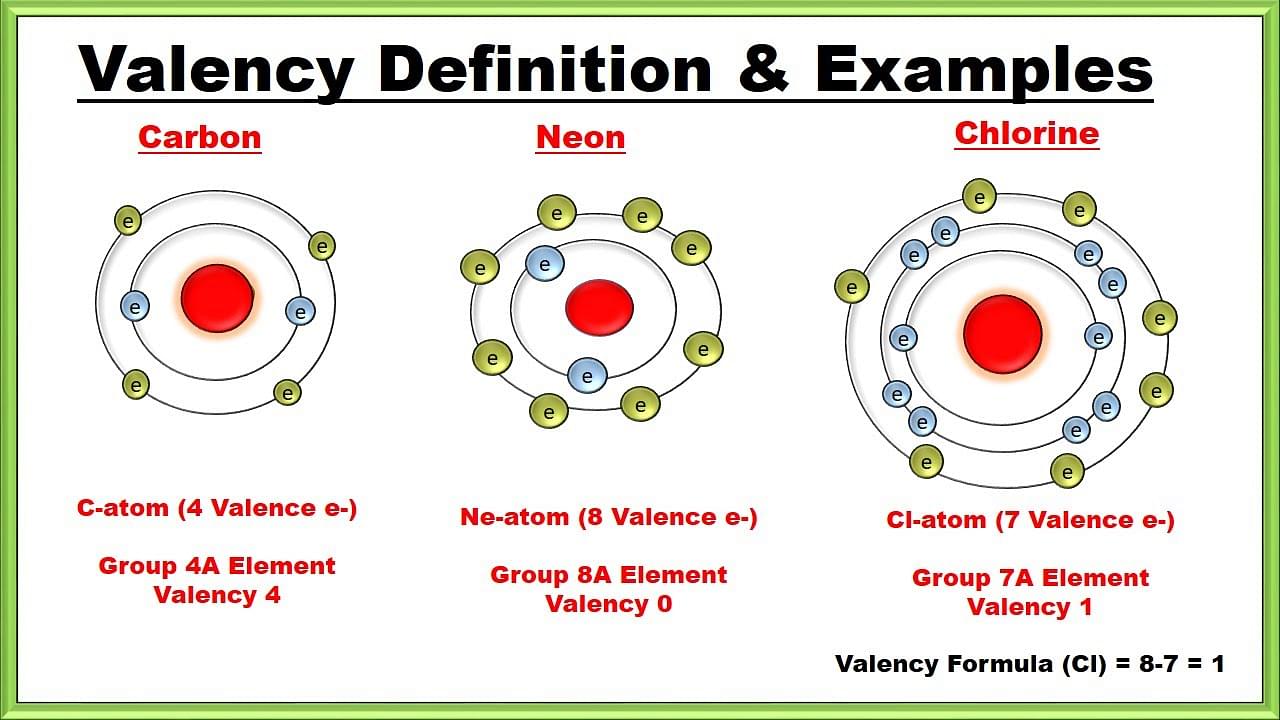
Valency, also known as valence, is a measure of the ability of an atom to form chemical bonds with other atoms. It is determined by the number of electrons an atom can gain, lose, or share in order to achieve a stable electron configuration, typically the electron configuration of a noble gas.
Here are some key points about valency:
Electron Configuration: Valency is related to the electron configuration of an atom, particularly the number of valence electrons—the electrons in the outermost energy level (shell) of the atom. The valence electrons are involved in chemical bonding and determine the atom's reactivity.
Noble Gas Configuration: Atoms tend to achieve a stable electron configuration similar to that of noble gases (group 18 elements) by gaining, losing, or sharing electrons. Noble gases have complete outer electron shells and are chemically inert. Other atoms seek to attain this stable configuration by either gaining or losing electrons to achieve a full outer shell, or by sharing electrons in covalent bonds.
Valence Electrons: The number of valence electrons an atom possesses determines its valency. For main group elements (groups 1, 2, 13-18), the valency is typically equal to the number of valence electrons. For transition metals and inner transition metals, determining valency can be more complex due to the presence of multiple oxidation states.
Oxidation Number: Valency is often expressed as the oxidation number of an atom in a compound. The oxidation number represents the charge an atom would have if electrons were transferred completely, rather than shared, in a chemical bond. It indicates the number of electrons an atom gains or loses when it forms a compound.
Determining Chemical Properties: Valency plays a crucial role in determining the chemical properties of elements and compounds. Atoms with similar valencies often exhibit similar chemical behaviors and tend to form similar types of chemical bonds.
Representation: Valency is commonly represented using Roman numerals or Greek letters to indicate the number of electrons gained, lost, or shared by an atom. For example, sodium (Na) has a valency of +1, chlorine (Cl) has a valency of -1, and oxygen (O) has a valency of -2.
In summary, valency is a measure of an atom's ability to form chemical bonds by gaining, losing, or sharing electrons in order to achieve a stable electron configuration. It is determined by the number of valence electrons an atom possesses and plays a key role in understanding the chemical behavior and reactivity of elements and compounds.
Thank you,