What is Data and Classification of Data?

Data:
- Data refers to raw facts, figures, symbols, or observations that represent the characteristics of people, objects, events, or any other entity. In its raw form, data may not provide any meaningful information. However, when processed, organized, and interpreted, data can turn into valuable information that informs decision-making, analysis, and understanding.
Classification of Data:

Data can be classified based on various attributes, including its nature, source, and use. The common classifications of data are as follows:
Based on Nature:

- Qualitative Data (Categorical Data): Qualitative data describes attributes, characteristics, or qualities that can be observed but not measured numerically. It uses non-numeric categories or labels to represent the information. Examples include names, colors, gender, types of animals, etc.
- Quantitative Data (Numerical Data): Quantitative data represents measurable quantities or numerical values. It deals with data that can be counted or measured. Examples include age, height, temperature, sales revenue, etc. Quantitative data can further be classified as:
- Discrete Data: Consists of whole numbers or countable values with distinct gaps between possible values. Examples include the number of students in a class, the number of cars sold, etc.
- Continuous Data: Represents values that can take any real number within a range. Examples include temperature, weight, time, etc.
Based on Source:

- Primary Data: Data collected directly from original sources through surveys, experiments, interviews, observations, etc.
- Secondary Data: Data obtained from existing sources, such as databases, publications, reports, or records that have been collected and analysed by others for different purposes.
Based on Use:

- Raw Data: Unprocessed and unorganised data as collected from its source.
- Processed Data: Data that has been organised, cleaned, and transformed into a usable format for analysis or presentation.
- Big Data: Extremely large datasets that require specialised techniques and technologies for storage, processing, and analysis due to their size and complexity.
- Metadata: Data that provides information about other data. It describes the characteristics, properties, and context of the actual data, facilitating understanding and management.
Based on Accessibility:
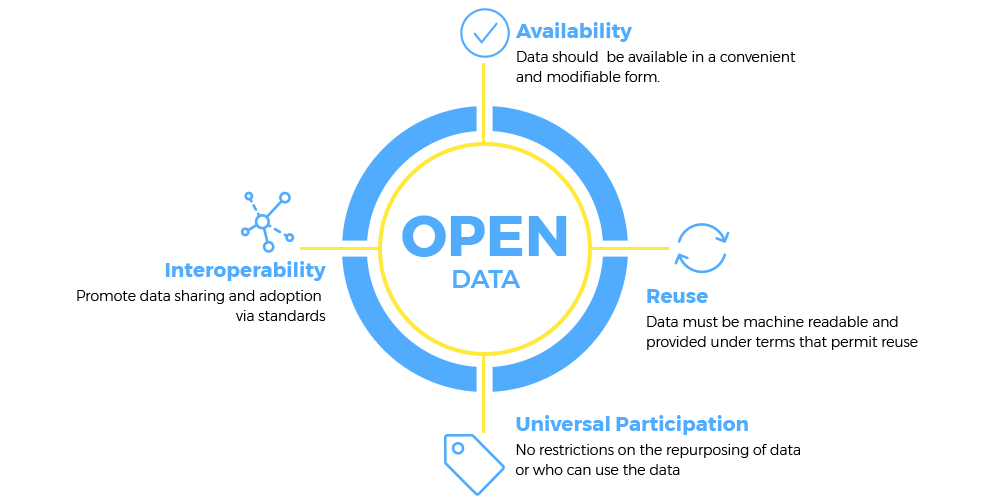
- Open Data: Data that is freely available for public use and can be accessed without any restrictions.
- Closed Data: Data that is restricted or not freely available to the public due to privacy, security, or confidentiality concerns.
Understanding the classification of data is essential in data analysis and processing, as different types of data may require distinct methods and techniques for handling and deriving valuable insights. Proper data classification ensures that data is effectively utilised to support decision-making and address various challenges in different fields.
Thank You





