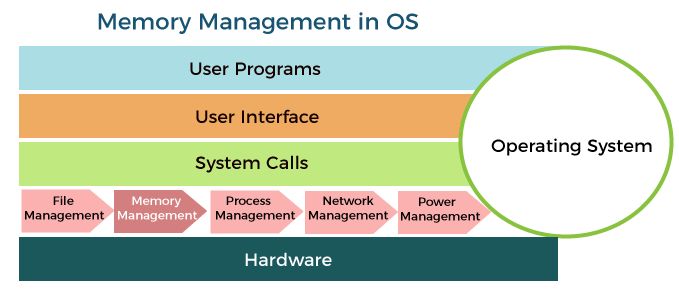
Memory management efficiency is a critical aspect of an operating system's performance, and it can vary depending on specific use cases and requirements. Both Linux and Windows, as well as other modern operating systems, have sophisticated memory management systems. The "best" operating system for memory management depends on the context of usage.
Here are some Considerations:
Linux: Linux is often praised for its memory management efficiency. It includes features such as:
Windows: Windows has improved its memory management over the years, and modern versions are efficient in utilizing available memory. Features include:
Real-time and Embedded Systems: Real-time operating systems (RTOS) and embedded systems have specialized memory management designed for low-latency and predictable response times.
Virtualization: Hypervisors like VMware, Xen, and KVM have their memory management techniques optimized for virtual machines.
Mainframe Operating Systems: Operating systems for mainframe computers, such as IBM z/OS, have advanced memory management features designed for high reliability and scalability.
Ultimately, the best choice for memory management depends on the specific needs of your application or use case. Factors like system hardware, software requirements, and workload characteristics will all play a role in determining the most suitable operating system for your memory management needs. In many cases, both Linux and Windows offer efficient memory management, and the choice may come down to other considerations, such as software compatibility, user interface, and community support.
Thank you.