IP (Internet Protocol) addresses are unique numerical labels assigned to devices connected to a computer network that uses the Internet Protocol for communication. There are two main types of IP addresses: IPv4 (Internet Protocol version 4) and IPv6 (Internet Protocol version 6), each serving a specific purpose in the modern Internet landscape.
Additionally, IP addresses can be categorized into different classes based on their intended use and allocation:
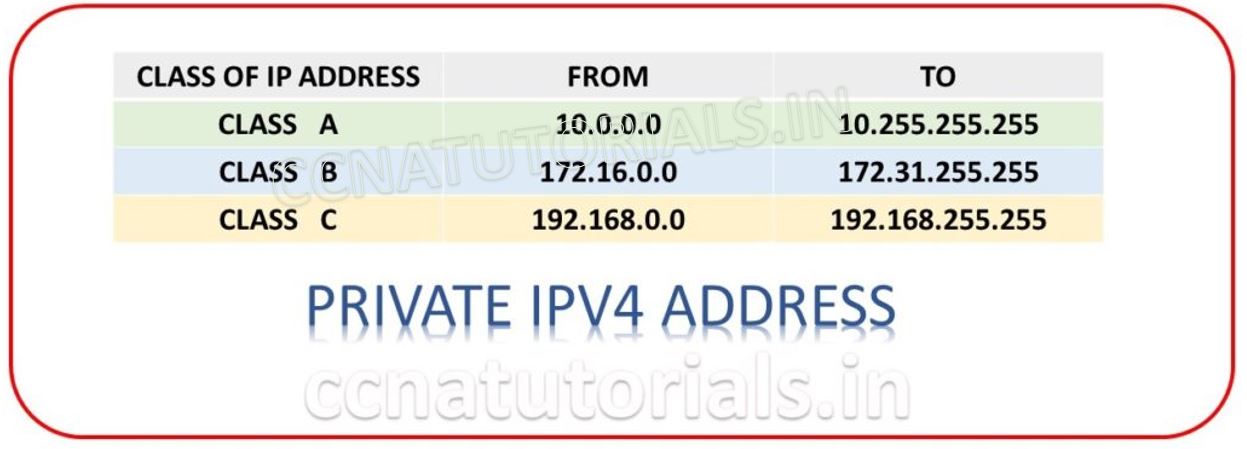
IPv4 Addresses:
IPv6 Addresses:
Special-Purpose IP Addresses:
Reserved IP Addresses:
Dynamic and Static IP Addresses:
These are the primary types and categories of IP addresses in use today. The transition to IPv6 is ongoing due to the depletion of available IPv4 addresses, and IPv6 addresses are becoming more prevalent as the internet continues to grow.
Thank You