Receipt Account
A Receipt Account is not a distinct formal financial statement or accounting term on its own but can refer to the following:
-
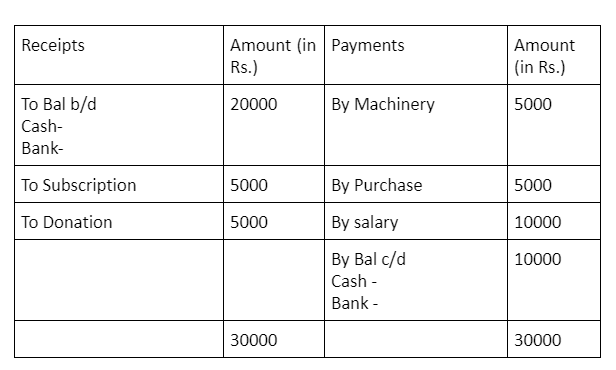
Part of Receipt and Payment Account:
- In the context of non-profit organizations and clubs, a Receipt Account could be interpreted as the section of a Receipt and Payment Account that lists all cash inflows or receipts during a specific period. This would include all sources of cash such as donations, membership fees, grants, sales of goods and services, and other income.
-
General Ledger Account:
- In a general ledger, a Receipt Account might be used to track specific types of cash receipts. For example, a business might have separate receipt accounts for different revenue streams like sales receipts, service receipts, or interest receipts.
-
Cash Receipts Journal:
- A cash receipts journal, sometimes informally referred to as a receipt account, records all cash inflows to the business. Each entry typically includes the date, amount, source of the receipt, and the account credited.
Key Features of Receipts in Accounting
-
Nature:
- Cash receipts represent money received by the organization or business. They increase the cash balance in the cash account.
-
Types of Receipts:
- Receipts can be classified into different categories based on their source, such as operational receipts (sales, service income), financial receipts (loan proceeds, interest income), and capital receipts (sale of assets, investment inflows).
-
Documentation:
- Proper documentation is crucial for each receipt transaction. This includes maintaining receipts, bank statements, and other supporting documents.
-
Recording:
- Receipts are recorded in the books of accounts at the time of actual receipt of cash or cash equivalents. This is typically done in the cash receipts journal or directly in the general ledger if the organization does not use specialized journals.
-
Reconciliation:
- Regular reconciliation of the receipt account or cash receipts journal with bank statements is essential to ensure accuracy and to identify any discrepancies or missing entries.
Example Entries
Here are some example entries for a cash receipts journal or receipt account:
-
Sales Receipt:
- Date: May 1, 2024
- Description: Cash sale
- Amount: $500
- Account Credited: Sales Revenue
-
Membership Fee:
- Date: May 2, 2024
- Description: Annual membership fee
- Amount: $200
- Account Credited: Membership Fees
-
Donation Received:
- Date: May 3, 2024
- Description: Donation from XYZ Foundation
- Amount: $1,000
- Account Credited: Donations
By maintaining a well-organized and detailed Receipt Account, businesses and organizations can effectively monitor and manage their cash inflows, ensuring financial stability and proper fund allocation.
Thank you,
