The Best Practices for Implementing an APM Framework
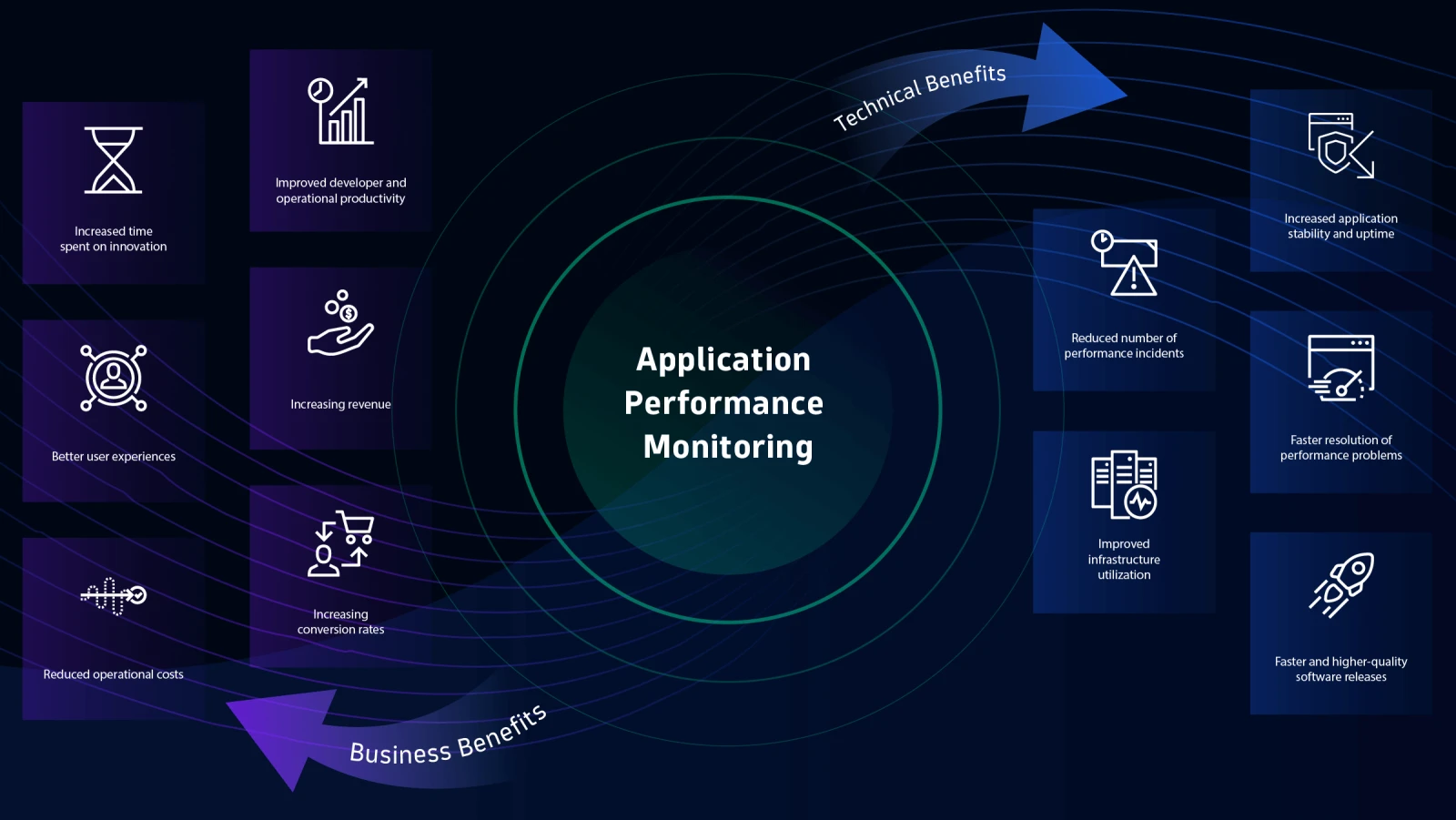
Implementing an Application Portfolio Management (APM) framework involves establishing processes, governance structures, and tools to effectively manage and optimize the organization's application portfolio. Here are some best practices for implementing an APM framework:
Define Clear Objectives and Scope: Clearly define the objectives and scope of the APM initiative, including the goals, stakeholders, timelines, and expected outcomes. Align APM objectives with broader IT and business strategies to ensure that the initiative delivers tangible value to the organization.
Establish Governance Structures: Establish governance structures to oversee the APM initiative, including roles, responsibilities, and decision-making processes. Define roles such as APM program sponsor, steering committee, portfolio manager, and governance board to provide oversight, guidance, and support throughout the implementation process.
Create a Comprehensive Inventory: Create a comprehensive inventory of applications within the organization, including details such as name, purpose, functionality, technology stack, usage, dependencies, ownership, and business impact. Ensure that the inventory is regularly updated to maintain accuracy and completeness.
Prioritize Applications: Prioritize applications based on their business value, strategic importance, technical health, and risk profile. Develop criteria and scoring mechanisms to prioritize applications for further analysis, investment, optimization, or retirement, aligning with business objectives and priorities.
Conduct Assessment and Analysis: Conduct a thorough assessment and analysis of the application portfolio to evaluate factors such as business value, technical health, usage patterns, dependencies, risks, and opportunities. Use a combination of quantitative and qualitative methods, including surveys, interviews, workshops, and data analysis, to gather insights and identify areas for improvement.
Develop Optimization Strategies: Develop optimization strategies and action plans to address findings from the assessment and analysis phase. This may include strategies for rationalizing the portfolio, consolidating redundant applications, modernizing legacy systems, adopting new technologies, and retiring obsolete applications. Prioritize initiatives based on their potential impact, feasibility, and alignment with strategic objectives.
Implement Governance Processes: Implement governance processes to manage the application lifecycle from inception to retirement effectively. Define processes for application intake, evaluation, prioritization, investment decision-making, implementation, monitoring, and continuous improvement. Ensure that governance processes are transparent, standardized, and aligned with organizational goals and policies.
Leverage Technology Solutions: Leverage technology solutions, such as APM software platforms, to support the implementation of the APM framework. Choose tools that provide capabilities for application discovery, inventory management, assessment, analysis, reporting, and governance to streamline APM processes and enhance decision-making.
Promote Collaboration and Communication: Promote collaboration and communication among stakeholders across different business units, IT teams, and executive leadership. Foster a culture of transparency, accountability, and knowledge sharing to ensure that APM initiatives are well-understood, supported, and embraced by all stakeholders.
Monitor and Measure Performance: Monitor and measure the performance and effectiveness of the APM framework over time. Define key performance indicators (KPIs) and metrics to track progress, evaluate outcomes, and identify areas for improvement. Use feedback from stakeholders and performance data to iterate on the APM framework and optimize its impact on the organization.
By following these best practices, organizations can implement an APM framework that effectively manages and optimizes the application portfolio, maximizes the value derived from IT investments, and drives business growth and innovation.
Thank you,