Criteria are used to Evaluate Applications Within a Portfolio
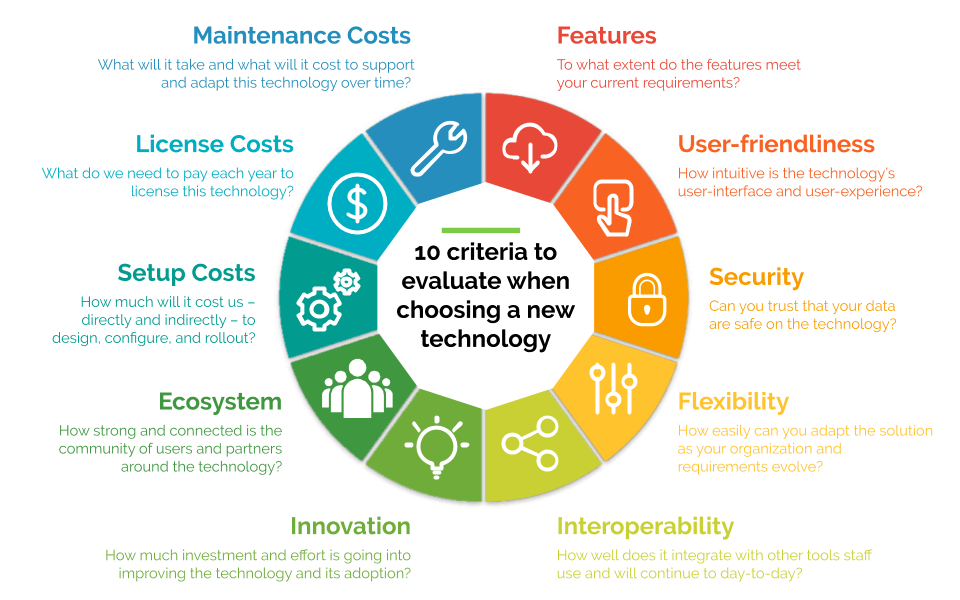
When evaluating applications within a portfolio, organizations typically consider a range of criteria to assess their performance, value, and alignment with business objectives. These criteria may vary depending on the organization's goals, industry, and specific context, but common evaluation criteria include:
Business Value: Assess the contribution of each application to the organization's strategic goals and objectives. Consider factors such as revenue generation, cost savings, customer satisfaction, market share, and competitive advantage.
Alignment with Business Objectives: Evaluate how well each application supports key business processes and initiatives. Consider factors such as alignment with strategic priorities, fit with organizational goals, and impact on business performance.
Usage and Adoption: Analyze the level of adoption and utilization of each application within the organization. Consider factors such as user engagement, frequency of use, user satisfaction, and feedback from stakeholders.
Technical Health: Assess the technical health and condition of each application. Consider factors such as scalability, performance, reliability, availability, security, compliance, and adherence to best practices.
Cost of Ownership: Evaluate the total cost of ownership (TCO) for each application, including acquisition costs, licensing fees, maintenance costs, support costs, infrastructure costs, and any associated expenses. Consider both direct and indirect costs over the application's lifecycle.
Risk Profile: Identify and assess risks associated with each application. Consider factors such as security vulnerabilities, compliance issues, dependencies on outdated technology, vendor stability, and potential impact on business operations in the event of failures or disruptions.
Strategic Fit: Evaluate the strategic fit of each application within the organization's IT landscape. Consider factors such as alignment with technology standards, architecture principles, integration requirements, and compatibility with other systems and applications.
Lifecycle Stage: Determine the lifecycle stage of each application, including maturity, relevance, and future viability. Consider factors such as age, obsolescence, supportability, and roadmap for future development and enhancements.
User Experience: Assess the user experience and usability of each application from the perspective of end-users. Consider factors such as ease of use, intuitiveness, accessibility, responsiveness, and satisfaction with the application's functionality and features.
Vendor Relationship: Evaluate the relationship with application vendors and service providers. Consider factors such as vendor reputation, reliability, responsiveness, support quality, contractual terms, and alignment with organizational values and objectives.
By evaluating applications against these criteria, organizations can gain a comprehensive understanding of their application portfolio, identify areas for improvement, and make informed decisions to optimize resource allocation, mitigate risks, and align technology investments with business priorities.
Thank you,