How does the IP Address work

An IP (Internet Protocol) address is a numerical label assigned to each device connected to a computer network that uses the Internet Protocol for communication. It serves two primary purposes:
Host or Network Identification:
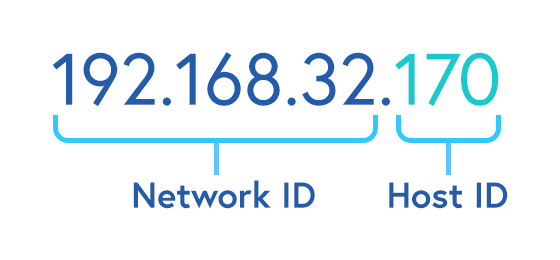
- IP addresses are used to uniquely identify devices within a network or on the internet. Just like a street address helps identify a location, an IP address identifies a device and its location on a network.
Routing of Data Packets:

- When data is transmitted over the internet or a network, it is broken down into smaller packets. Each packet contains the source IP address (where it comes from) and the destination IP address (where it's going to). Routers and other networking devices use these IP addresses to direct the packets to the correct destination.
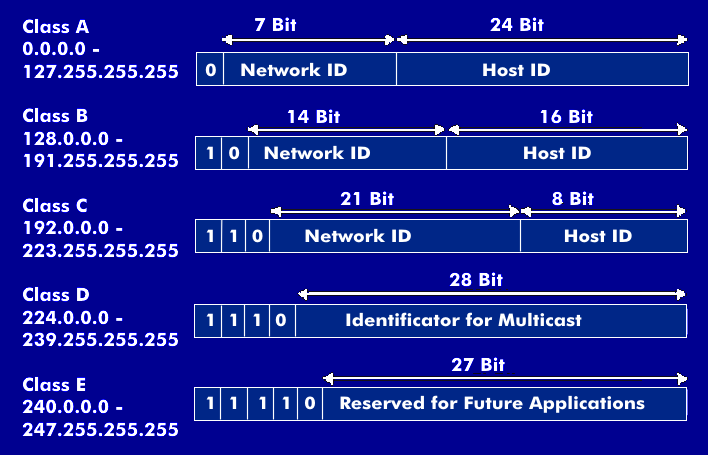
- IP addresses are typically 32-bit or 128-bit binary numbers. However, for human convenience, they are often represented in a dotted-decimal format, such as IPv4 (32-bit) or IPv6 (128-bit). For example:
- IPv4: 192.168.0.1
IPv6: 2001:0db8:85a3:0000:0000:8a2e:0370:7334
- IPv4 is the older and most widely used version. It consists of four sets of numbers, each ranging from 0 to 255, separated by dots (e.g., 192.168.0.1). However, due to the rapid growth of the internet and the depletion of available IPv4 addresses, a newer version called IPv6 was introduced. IPv6 uses a longer address format (e.g., 2001:0db8:85a3:0000:0000:8a2e:0370:7334) and provides an almost inexhaustible number of unique addresses.
- When you connect your device (e.g., a computer, smartphone, or any internet-enabled gadget) to the internet, your Internet Service Provider (ISP) assigns you an IP address. This can be a dynamic IP address, meaning it changes over time, or a static IP address, which remains constant. When you request data from a website or any other online service, your IP address is included in the data packets, allowing the response to be sent back to your device.
In summary, IP addresses are the backbone of communication on the internet, allowing devices to find and communicate with each other across vast networks. They provide the foundation for delivering data packets to their intended destinations, ensuring that data reaches the correct device on a network.


