Microscopes
Microscopes are essential tools used in scientific research, medical diagnostics, and various other fields to magnify and visualize objects that are otherwise invisible to the naked eye. There are several types of microscopes, each designed for specific applications and offering unique capabilities. Here are some common types of microscopes:
Optical Microscopes:

- Compound Microscopes: These microscopes use multiple lenses to magnify small specimens. They are widely used in biology, medicine, and materials science.
- Stereo Microscopes: Also known as dissecting microscopes, stereo microscopes provide a three-dimensional view of larger objects at lower magnifications. They are commonly used for tasks like dissection, circuit board inspection, and jewelry examination.
Electron Microscopes:
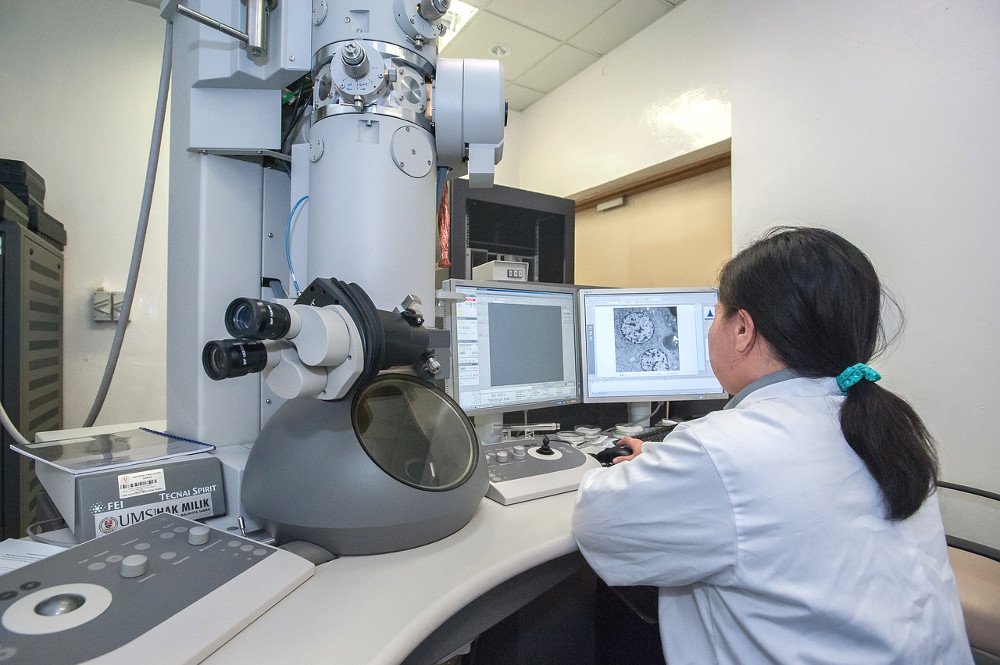

- Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM): SEMs use a focused beam of electrons to scan the surface of a specimen, producing high-resolution, three-dimensional images. They are used for studying surface structures and topography.
- Transmission Electron Microscope (TEM): TEMs transmit a beam of electrons through a thin specimen to create highly detailed internal images. They are used for studying the ultrastructure of cells, viruses, and various materials.
Scanning Probe Microscopes:
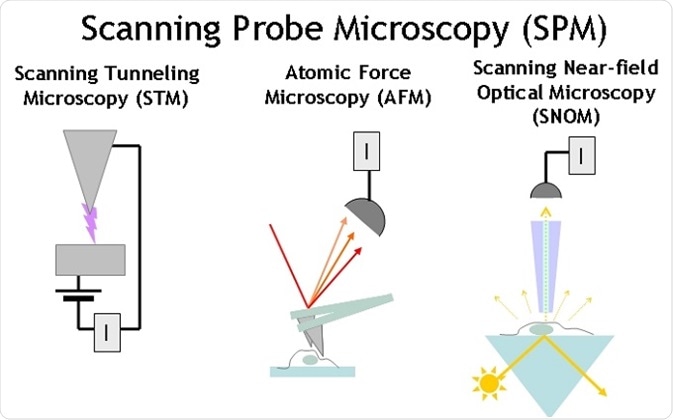
- Atomic Force Microscope (AFM): AFMs use a tiny probe to scan the surface of a specimen, measuring the forces between the probe and the sample. They provide high-resolution images and can even manipulate individual atoms.
- Scanning Tunneling Microscope (STM): STMs operate by scanning a conductive probe very close to the specimen surface, measuring the flow of electrons between the probe and the surface. They are primarily used to study conductive materials at the atomic scale.
Confocal Microscopes:

- Confocal microscopes use laser illumination and a pinhole aperture to eliminate out-of-focus light, resulting in enhanced optical sectioning and three-dimensional imaging capabilities. They are widely used in biological research for imaging fluorescently labeled specimens.
Fluorescence Microscopes:
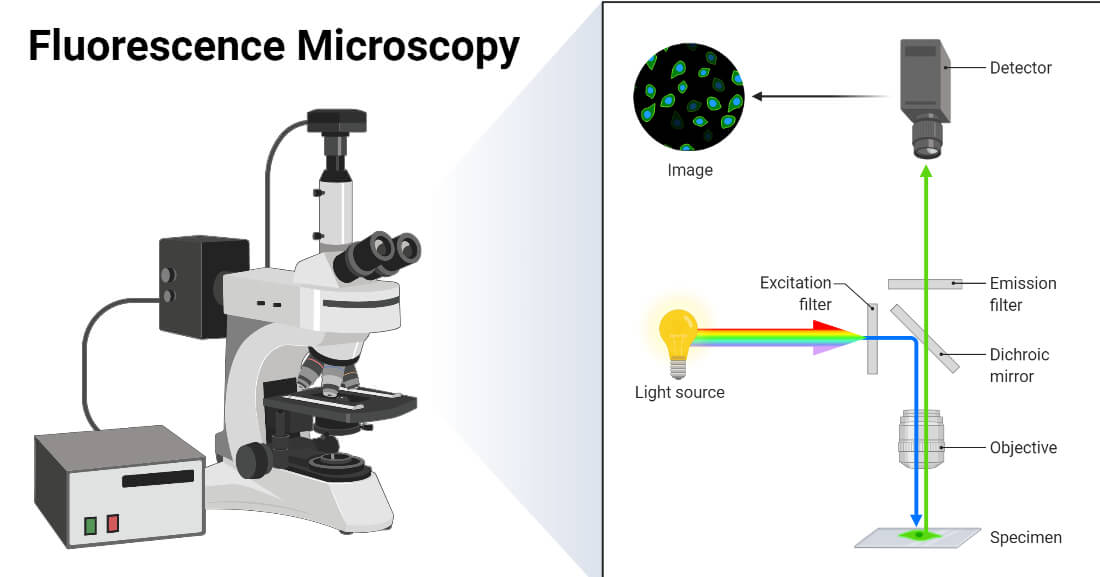
- These microscopes use fluorescence techniques to observe and study specimens that emit light of specific wavelengths when illuminated with light of a different wavelength. They are used extensively in biological research and medical diagnostics.
Phase-Contrast Microscopes:
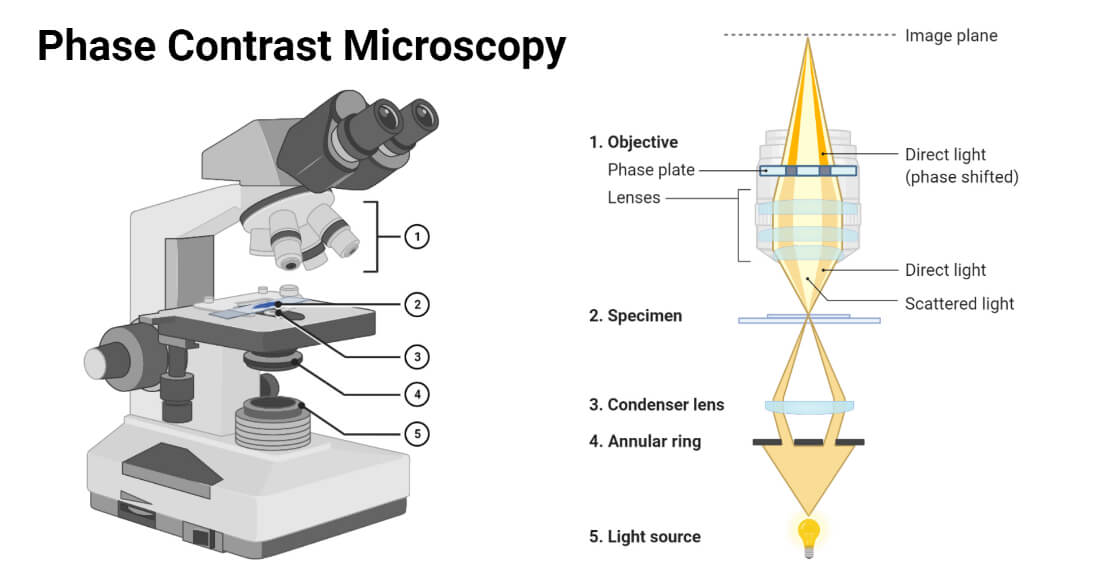
- Phase-contrast microscopes enhance the contrast of transparent and colorless specimens, such as live cells, by exploiting differences in the refractive index of different parts of the specimen.
Polarizing Microscopes:

- Polarizing microscopes use polarized light to study the optical properties of materials, such as crystals and minerals. They are commonly used in geology, petrology, and materials science.
These are just a few examples of the many types of microscopes available. Each type has its own strengths and applications, allowing scientists and researchers to explore the microscopic world in diverse ways.
Thank You.






