LAN
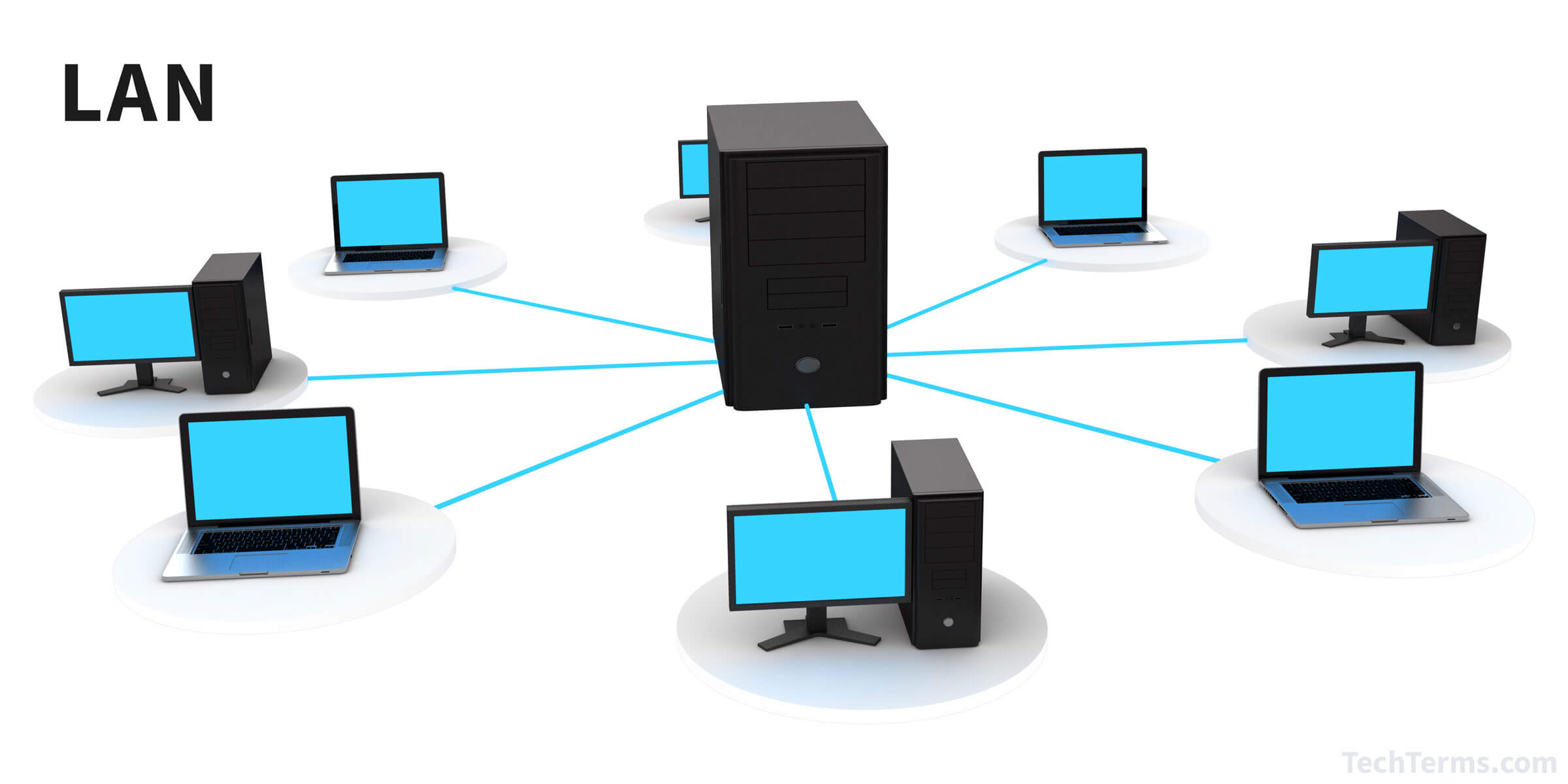
LAN stands for Local Area Network. It refers to a network of computers and other devices that are interconnected within a limited geographical area, such as a home, office building, school, or small campus. LANs allow connected devices to communicate and share resources, such as files, printers, and internet access, facilitating data exchange and collaboration among users.
Key characteristics of LANs include:
Limited Geographic Area: LANs typically cover a relatively small area, such as a single building or group of buildings in close proximity. They are designed to serve the networking needs of users within this confined area.
High Speed: LANs often provide high-speed data transmission rates, allowing for fast communication and data transfer between connected devices. This is essential for supporting applications that require real-time or near-real-time interaction, such as video streaming, online gaming, and VoIP (Voice over Internet Protocol) calls.
Private Ownership: LANs are usually privately owned and managed by an organization, such as a company, educational institution, or government agency. The owner is responsible for configuring and maintaining the network infrastructure, ensuring its security and reliability.
Topology: LANs can be configured in various network topologies, including star, bus, ring, and mesh. The topology determines how devices are connected to one another and how data flows within the network.
Ethernet and Wi-Fi: LANs can be implemented using wired or wireless technologies. Ethernet, which uses cables and switches, is a common choice for wired LANs. Wi-Fi, based on wireless radio signals, is widely used for wireless LANs, providing flexibility and mobility for connected devices.
Resource Sharing: One of the primary purposes of LANs is to facilitate resource sharing among connected devices. Users can share files, printers, internet connections, and other network resources, enhancing productivity and collaboration within the local network environment.
Overall, LANs play a crucial role in modern networking infrastructure, providing a means for devices within a limited geographic area to communicate, share resources, and access services efficiently. They form the foundation for many local and wide-area network deployments, enabling connectivity and data exchange in various personal, professional, and educational settings.
Thank you,