Examples of Operating Models
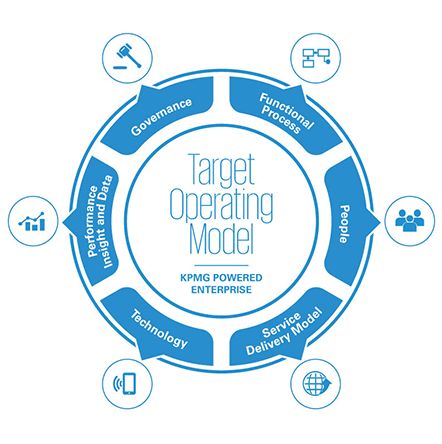
Operating models can vary significantly across industries, organizations, and contexts. Here are some examples of operating models in different sectors:
-
Manufacturing Operating Model:
- In a manufacturing company, the operating model may include processes for procurement of raw materials, production scheduling, inventory management, quality control, and distribution.
- The structure might consist of production lines or cells organized by product type or production process, with roles such as production workers, supervisors, quality inspectors, and maintenance staff.
- Key capabilities may include lean manufacturing techniques, just-in-time inventory management, and continuous improvement initiatives such as Six Sigma.
- Governance mechanisms could involve regular production meetings, performance dashboards tracking metrics like throughput and defect rates, and cross-functional teams for problem-solving.
-
Retail Operating Model:
- A retail operating model may encompass processes for merchandising, store operations, sales, customer service, and supply chain management.
- The structure might include store formats such as brick-and-mortar stores, e-commerce platforms, and mobile apps, with roles such as store associates, managers, buyers, and logistics coordinators.
- Key capabilities may include inventory management systems, customer relationship management (CRM) software, and omnichannel retailing strategies.
- Governance mechanisms might include regular sales and inventory reviews, customer feedback mechanisms, and performance metrics such as sales per square foot and inventory turnover.
-
Technology Company Operating Model:
- In a technology company, the operating model may involve processes for product development, software engineering, product management, sales and marketing, and customer support.
- The structure might consist of cross-functional teams organized around products or projects, with roles such as product managers, engineers, designers, marketers, and customer success managers.
- Key capabilities may include agile development methodologies, DevOps practices, and customer-centric design principles.
- Governance mechanisms could include regular sprint reviews, product roadmap planning sessions, and performance metrics such as time-to-market and customer satisfaction scores.
-
Financial Services Operating Model:
- In a financial services firm, the operating model may encompass processes for banking operations, risk management, compliance, investment management, and customer relationship management.
- The structure might include business units such as retail banking, wealth management, investment banking, and risk management, with roles such as bankers, advisors, traders, analysts, and compliance officers.
- Key capabilities may include automated banking systems, risk assessment models, and regulatory compliance frameworks.
- Governance mechanisms might include risk committees, compliance audits, and performance metrics such as return on assets and capital adequacy ratios.
These examples illustrate how operating models can be tailored to specific industries and organizational contexts to support strategic objectives, streamline operations, and deliver value to customers and stakeholders.
Thank you,