Types of Floods
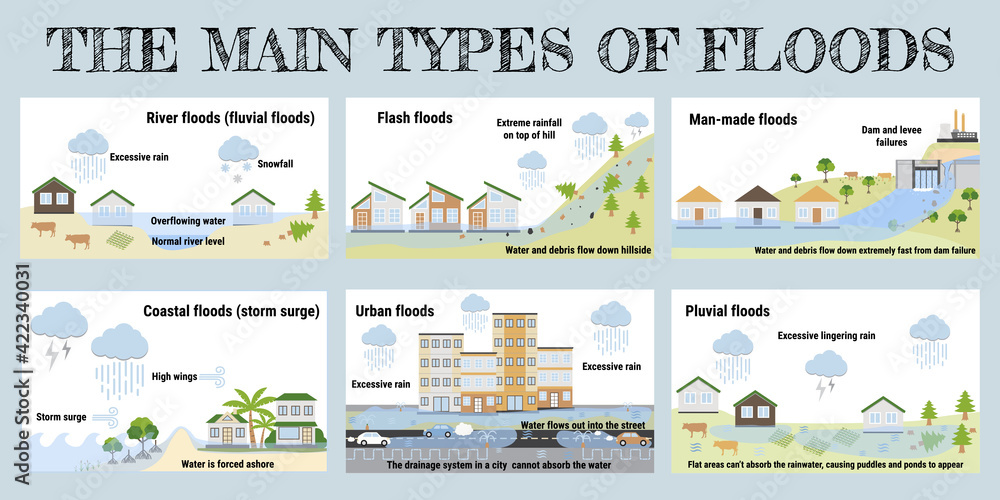
Floods can be categorized into various types based on their causes, characteristics, and locations. Here are some common types of floods:
River Floods: These occur when water levels in rivers exceed their banks, leading to the inundation of adjacent land. River floods can result from prolonged heavy rainfall, snowmelt, or a combination of factors.
Flash Floods: Flash floods are sudden and intense floods that can occur within minutes or hours of heavy rainfall or the sudden release of water. They often occur in areas with steep terrain, urban areas with poor drainage, or in regions where the soil is already saturated.
Coastal Floods: Coastal or tidal floods are caused by storm surges, high tides, or tsunamis. They can lead to the inundation of coastal areas, posing a threat to both human settlements and ecosystems.
Urban Floods: Urban flooding is associated with heavy rainfall overwhelming drainage systems in urban areas. Impervious surfaces, such as concrete and asphalt, prevent water absorption, leading to rapid runoff and increased flooding risk.
Pluvial Floods: Pluvial floods result from heavy rainfall that exceeds the capacity of the local drainage system, leading to surface water flooding in urban or rural areas.
Dam or Levee Break Floods: The failure of dams or levees can cause catastrophic flooding downstream. This can occur due to structural failure, overtopping, or erosion of these structures.
Ice Jam Floods: In cold climates, rivers can experience ice jams, where ice accumulates and blocks the flow of water. When the blockage breaks, it can lead to sudden flooding.
Flash Droughts: While not commonly discussed, flash droughts involve rapid and severe onset of drought conditions, leading to water shortages. This can contribute to conditions that increase the risk of wildfires and impact water resources.
Monsoonal Floods: In regions experiencing a monsoon climate, heavy and prolonged rainfall during the monsoon season can lead to riverine and flash flooding.
Understanding the specific characteristics of each type of flood is crucial for developing effective mitigation strategies and response plans. Different regions may be more prone to certain types of floods based on their geography, climate, and land use.
Thank you.