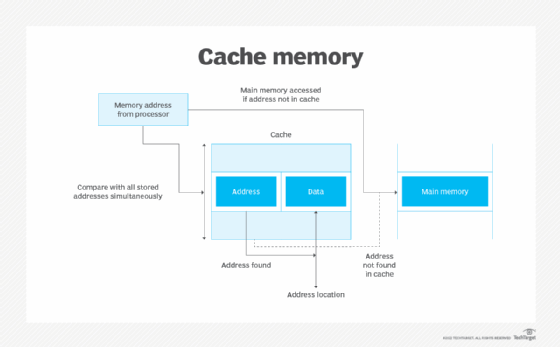
Cache memory plays a crucial role in computer systems by providing high-speed storage for frequently accessed data and instructions. Its primary function is to enhance the overall performance of the system by reducing the time it takes for the central processing unit (CPU) to access data from the slower main memory (RAM) or even slower storage devices like hard drives.
Here are the key roles and functions of Cache Memory in a Computer:
Faster Data Access: Cache memory stores frequently used data, instructions, and program code that the CPU requires for processing. Since cache memory is much faster than main memory, accessing data from the cache reduces the time it takes for the CPU to retrieve information, resulting in faster execution of programs.
Reduced Memory Latency: Cache memory minimizes memory access latency, as it is physically closer to the CPU than main memory. This low-latency access to data and instructions means that the CPU can operate more efficiently and perform tasks more quickly.
Improved System Responsiveness: Caching frequently used data and code leads to improved system responsiveness and smoother user experiences. Commonly used applications, libraries, and system routines are often cached, enhancing the overall user experience.
Lower CPU Wait Time: Without cache memory, the CPU might spend significant time waiting for data from main memory. Cache reduces CPU wait times, allowing it to stay busy and process instructions more rapidly.
Reduced Power Consumption: Caching data and instructions can lead to lower power consumption, as it enables the CPU to operate more efficiently. This can be important in battery-powered devices and mobile computing.
Optimized Resource Utilization: Cache memory helps in optimizing resource utilization, as it ensures that the CPU operates at or near its full capacity without being idle due to memory access delays.
Multi-Level Caching: Modern CPUs often use multiple levels of cache (L1, L2, and sometimes L3 caches) to provide hierarchical storage for frequently accessed data. The L1 cache, closest to the CPU core, contains the most critical data, while the L3 cache, which is shared among CPU cores, holds larger amounts of data.
Cache Coherency: In multi-core processors, cache memory plays a role in ensuring cache coherency. It ensures that multiple CPU cores see consistent views of shared memory to maintain data integrity and avoid conflicts.
Dynamic Data Management: Some cache systems employ dynamic management strategies to determine which data to store. These strategies adapt to the usage patterns of the CPU, ensuring that the most relevant data is always available in the cache.
Cache Replacement Policies: Cache memory uses replacement policies (e.g., Least Recently Used - LRU) to determine which data should be evicted from the cache when new data needs to be stored.
Cache Memory is a critical component in modern computer architectures, and its design and management have a significant impact on overall system performance. It bridges the speed gap between the CPU and main memory, allowing computers to execute instructions more efficiently and provide faster response times to users.
Thank you.