Types of Brute Force Attacks
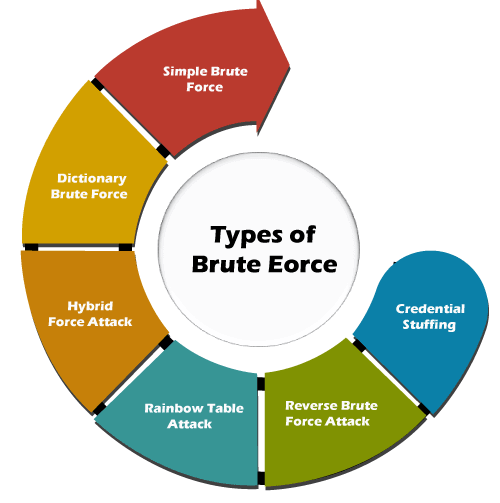
Brute force attacks can be categorized into different types based on the target, the method used, or the specific vulnerabilities exploited. Here are some common types of brute force attacks:
Simple Brute Force Attack: This is the most straightforward type of brute force attack, where the attacker systematically tries all possible combinations of characters until the correct one is found. This method is often used to guess passwords for user accounts or encryption keys.
Dictionary Attack: In a dictionary attack, the attacker uses a predefined list of words, phrases, or commonly used passwords (the dictionary) to guess the password. This approach is more efficient than a simple brute force attack since it reduces the search space to likely candidates.
Credential Stuffing: Credential stuffing involves using lists of previously stolen usernames and passwords obtained from data breaches to try to gain unauthorized access to other accounts. Attackers automate the login process using these stolen credentials on various websites or services, exploiting users who reuse passwords across multiple accounts.
Reverse Brute Force Attack: In a reverse brute force attack, the attacker fixes a single password and systematically tries different usernames or account identifiers until a match is found. This method is often used when the attacker knows or suspects a common password but needs to find a valid username to access an account.
Hybrid Attack: A hybrid attack combines elements of brute force and dictionary attacks. It involves trying variations of dictionary words or known passwords, such as appending numbers or special characters, to increase the chances of success.
Incremental Brute Force Attack: In an incremental brute force attack, the attacker starts with a certain character set (e.g., lowercase letters) and iteratively adds additional characters until the correct password is found. This method allows attackers to prioritize shorter passwords before attempting longer ones, optimizing the search process.
Rainbow Table Attack: While not strictly a brute force attack, a rainbow table attack involves precomputing a large database of hashes for commonly used passwords or character combinations. Attackers then compare the hash of the target password to entries in the rainbow table to find a match quickly, bypassing the need to perform extensive computation during the attack.
Each type of brute force attack has its own characteristics, targets, and methods, but they all share the common goal of systematically guessing passwords or authentication credentials to gain unauthorized access to systems, networks, or accounts. Implementing strong security measures, such as complex passwords, account lockout policies, and multi-factor authentication, can help mitigate the risk of brute force attacks.
Thank you,