What is Differential GPS (DGPS)
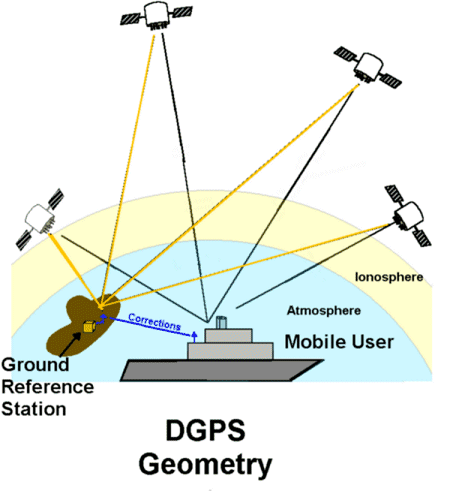
Differential GPS (DGPS) is an enhancement to the Global Positioning System (GPS) that improves the accuracy of GPS positioning by correcting errors caused by atmospheric effects, satellite orbit inaccuracies, and other sources of GPS signal degradation. DGPS works by comparing the measured positions from a reference station with known coordinates to the positions calculated by a GPS receiver, and then transmitting correction data to the receiver to improve its accuracy. Here's how Differential GPS works:
Reference Station: A reference station with precisely known coordinates is established at a known location. The reference station continuously monitors GPS signals from satellites and calculates its own position using the same satellite signals received by GPS receivers.
Error Determination: The reference station compares its calculated position with its known coordinates to determine the errors in GPS positioning. These errors may include ionospheric delay, tropospheric delay, satellite clock errors, and other sources of GPS signal degradation.
Correction Calculation: The reference station calculates correction values for the measured errors in GPS positioning. These correction values are typically transmitted to nearby GPS receivers using a radio link or other communication method.
Correction Transmission: The correction values are transmitted to DGPS-enabled GPS receivers located within the coverage area of the reference station. The correction data may be transmitted in real-time or stored for later retrieval by the receivers.
Receiver Correction: The DGPS receiver receives the correction data and applies it to the GPS position calculations. By applying the correction values to the raw GPS measurements, the receiver corrects for errors and improves the accuracy of its calculated position.
Improved Positioning Accuracy: With the correction data from the reference station, the DGPS receiver achieves higher accuracy positioning than would be possible with standalone GPS. The accuracy improvement can range from a few meters to sub-meter or centimeter-level accuracy, depending on the quality of the correction data and the distance from the reference station.
DGPS is commonly used in applications that require precise positioning, such as land surveying, precision agriculture, marine navigation, and aviation. It enhances the reliability and accuracy of GPS positioning in environments where standard GPS may be affected by factors such as atmospheric conditions, signal blockage, or satellite geometry.
Thank you,