What is an Operating System and what Functions does it Perform
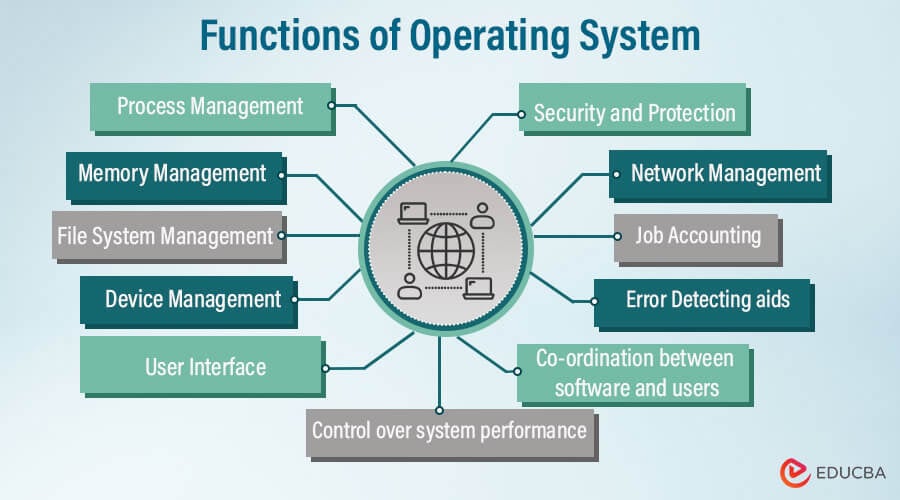
An operating system (OS) is system software that manages computer hardware and provides a platform for running applications. It acts as an intermediary between users and computer hardware, facilitating communication and interaction between the two. Here are some key functions performed by an operating system:
-
Process Management:
- The OS manages processes, which are instances of executing programs. It allocates CPU time to processes, schedules their execution, and ensures that they run efficiently.
- Process management includes functions such as process creation, termination, suspension, and synchronization.
-
Memory Management:
- The OS manages system memory (RAM) to ensure that each process has sufficient memory to execute.
- It allocates memory to processes, tracks memory usage, and handles memory fragmentation.
- Memory management also includes virtual memory techniques like paging and segmentation to optimize memory usage and provide a larger address space than physical RAM.
-
File System Management:
- The OS provides a file system that organizes and manages files stored on storage devices such as hard drives, SSDs, and flash drives.
- File system management includes functions such as file creation, deletion, reading, writing, and access control.
- It also handles directory structure, file metadata, and file permissions.
-
Device Management:
- The OS manages input/output (I/O) devices such as keyboards, mice, printers, network adapters, and storage devices.
- It provides device drivers that enable communication between software applications and hardware devices.
- Device management involves detecting and configuring devices, handling device interrupts, and managing device access and resources.
-
User Interface:
- The OS provides a user interface that allows users to interact with the computer and its applications.
- User interfaces can be command-line interfaces (CLI) where users type commands, or graphical user interfaces (GUI) with windows, icons, menus, and pointers (WIMP).
- User interface functions include displaying information, accepting user input, and managing windows and graphical elements.
-
Security and Access Control:
- The OS enforces security policies to protect system resources and data from unauthorized access and malicious activities.
- It implements user authentication mechanisms such as passwords, encryption, and access control lists (ACLs) to control user access to files and system resources.
- Security features also include firewall management, antivirus software integration, and system integrity checks.
-
System Administration:
- The OS provides tools and utilities for system administration tasks such as system configuration, software installation, user management, and performance monitoring.
- System administrators use these tools to manage and maintain the system, troubleshoot issues, and ensure smooth operation.
Overall, the operating system plays a crucial role in managing computer resources, providing a stable and secure environment for running applications, and facilitating user interaction with the computer system.
Thank you,
