The Temperature Change During Summer in Different Regions
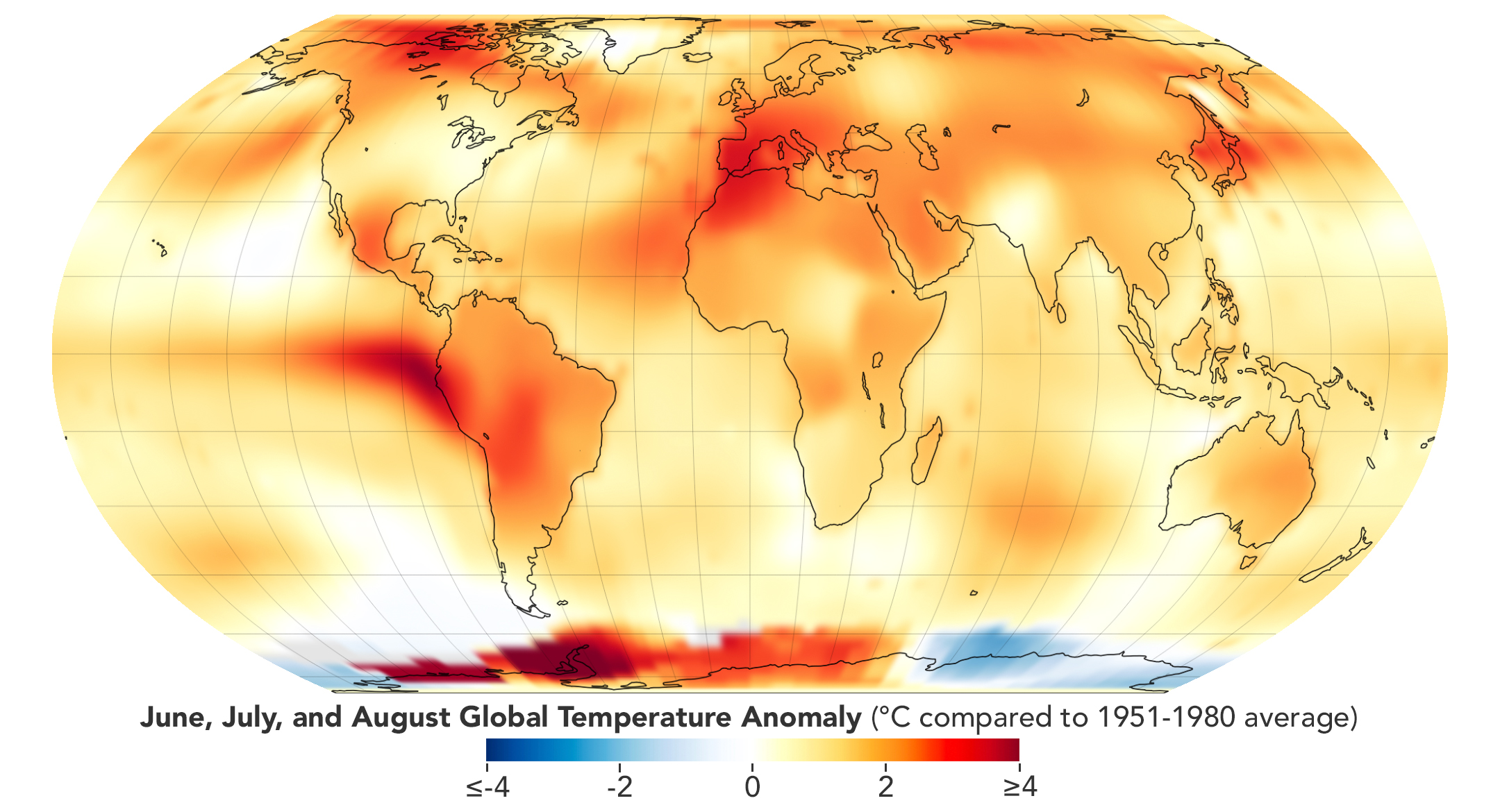
The temperature changes during the summer season can vary significantly between different regions due to factors such as latitude, altitude, proximity to bodies of water, and local climate patterns. Here's how the temperature change during summer varies across different regions:
-
Temperate Regions:
- In temperate regions, such as those located in the mid-latitudes, summer temperatures typically rise compared to the preceding spring months.
- Daytime highs in temperate regions during summer can vary widely, ranging from mild to hot temperatures depending on factors such as location, elevation, and proximity to oceans or mountains.
- Coastal areas in temperate regions often experience cooler temperatures during the summer due to the moderating influence of nearby bodies of water, such as oceans or large lakes.
- Inland areas away from coastal influences may experience more significant temperature fluctuations, with hotter daytime temperatures and cooler nighttime temperatures.
-
Tropical Regions:
- In tropical regions near the equator, summer temperatures remain consistently warm throughout the year due to the region's proximity to the Sun and minimal seasonal variations in sunlight angle.
- Summer in tropical regions is often characterized by high temperatures, high humidity, and frequent afternoon thunderstorms or showers.
- Coastal areas in tropical regions may experience slightly cooler temperatures compared to inland areas, thanks to the cooling effects of sea breezes and the moderating influence of the ocean.
-
Arctic and Subarctic Regions:
- In Arctic and subarctic regions located at high latitudes, summer temperatures can increase significantly compared to the colder winter months.
- Despite the increase in temperatures, summer temperatures in Arctic and subarctic regions generally remain cool relative to temperate and tropical regions, with daytime highs often ranging from cool to mild.
- In these regions, summer is characterized by the melting of snow and ice, the emergence of vegetation, and the return of wildlife as temperatures become more conducive to life.
-
Mountainous Regions:
- In mountainous regions, summer temperatures can vary widely based on altitude, with cooler temperatures at higher elevations and warmer temperatures in valleys and foothills.
- Summer temperatures in mountainous regions are influenced by factors such as elevation, topography, and local climate patterns, leading to diverse microclimates and temperature gradients across different elevations.
Overall, the temperature changes during summer vary across different regions due to a combination of geographic, climatic, and environmental factors. Understanding these variations is essential for predicting and preparing for the diverse weather conditions associated with the summer season in different parts of the world.
Thank you,
