How does Solar Energy Work
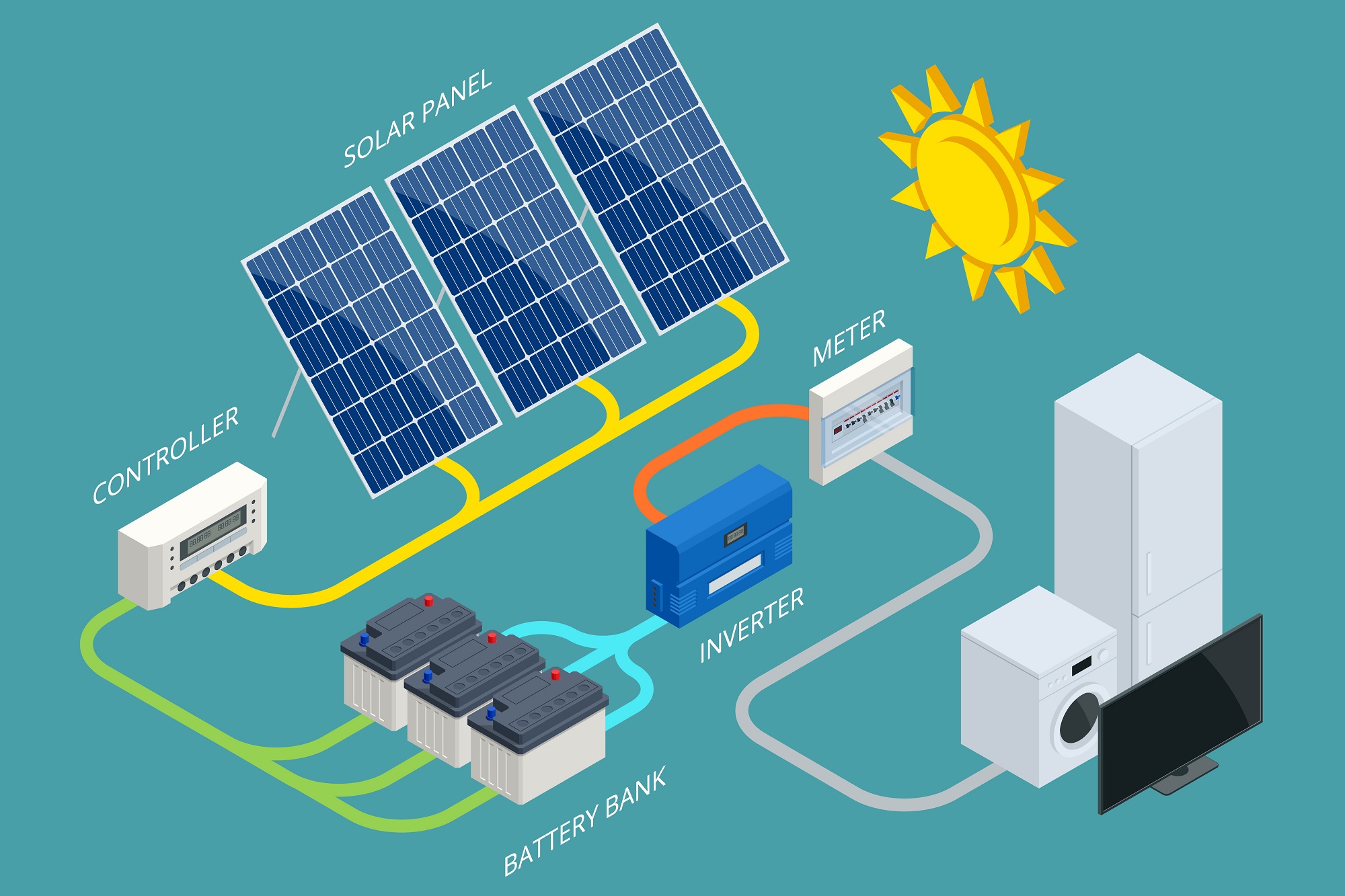
Solar energy works through the conversion of sunlight into usable forms of energy, such as electricity or heat. The process involves various technologies and components depending on the specific application, but the fundamental principles remain consistent. Here's how solar energy works in two primary applications: solar photovoltaic (PV) systems and solar thermal systems:
Solar Photovoltaic (PV) Systems:
Photovoltaic Cells: These are the basic building blocks of solar panels. They are made of semiconductor materials, such as silicon, which have special properties that allow them to convert sunlight into electricity. When sunlight hits the photovoltaic cells, it excites the electrons within the material, creating an electric current.
Solar Panels: Photovoltaic cells are interconnected and encapsulated within solar panels. Solar panels are typically composed of multiple solar cells arranged in a grid-like pattern. When sunlight strikes the solar panels, the photovoltaic cells generate direct current (DC) electricity.
Inverter: Since most household appliances and the electricity grid operate on alternating current (AC), the DC electricity produced by solar panels needs to be converted into AC. This conversion is done by an inverter, which is typically installed near the main electrical panel of a home or building.
Electricity Usage or Grid Connection: The AC electricity produced by the solar panels can be used immediately to power electrical devices within the building. Any excess electricity generated can be fed back into the grid if the system is connected to it. Alternatively, energy storage systems, such as batteries, can store excess electricity for use during times when sunlight is not available.
Solar Thermal Systems:
Solar Collectors: In solar thermal systems, solar collectors capture sunlight and convert it into heat. These collectors can be flat-plate collectors or concentrating collectors, depending on the specific application.
Heat Transfer Fluid: The captured sunlight heats a fluid (usually water or a heat transfer fluid like oil) circulating within the solar collectors. The heated fluid carries thermal energy to a heat exchanger.
Heat Exchanger: The heat exchanger transfers the thermal energy from the fluid to a medium used for the intended application, such as water for domestic hot water systems or a heat transfer fluid for industrial processes.
Storage (Optional): Some solar thermal systems include thermal energy storage to store excess heat for use when sunlight is not available, providing continuous availability of hot water or thermal energy.
Both solar PV and solar thermal systems harness the abundant energy from the sun to provide clean and renewable power for various applications, contributing to a more sustainable energy future.
Thank you,