Cloud Hypervisor
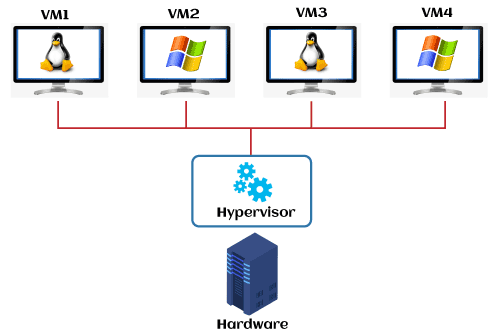
A cloud hypervisor refers to a hypervisor specifically designed and optimized for virtualization in cloud computing environments. Cloud hypervisors play a crucial role in managing and orchestrating virtualized resources within cloud infrastructure. They enable the creation, deployment, and efficient management of virtual machines (VMs) in cloud environments.
Key characteristics and features of cloud hypervisors include:
-
Multi-Tenancy Support:
- Cloud hypervisors are designed to support multi-tenancy, allowing multiple users or organizations to share the same physical infrastructure while maintaining isolation between their virtualized environments.
-
Resource Pooling:
- Cloud hypervisors facilitate the pooling of physical resources such as CPU, memory, storage, and network bandwidth. These resources are dynamically allocated to virtual machines based on demand.
-
Elasticity and Scalability:
- Cloud hypervisors enable the dynamic scaling of resources to accommodate changing workloads. This scalability is a key feature of cloud computing, allowing users to scale up or down as needed.
-
Live Migration:
- Cloud hypervisors often support live migration, allowing virtual machines to be moved from one physical host to another without service interruption. Live migration contributes to load balancing and facilitates hardware maintenance without downtime.
-
Snapshot and Cloning:
- Cloud hypervisors support features such as VM snapshots and cloning. Snapshots enable the creation of point-in-time copies of VM states, while cloning allows for the quick duplication of VMs.
-
Integration with Cloud Management Platforms:
- Cloud hypervisors are typically integrated with cloud management platforms and orchestration tools. These tools provide a higher-level interface for provisioning, managing, and monitoring virtualized resources in the cloud.
-
Security and Compliance:
- Cloud hypervisors implement security measures to ensure the isolation of virtualized environments and compliance with regulatory requirements. This includes features such as secure boot, encryption, and network security.
-
Performance Optimization:
- Cloud hypervisors are optimized for performance in cloud environments, aiming to maximize resource utilization and efficiency. They often include features like paravirtualization and hardware-assisted virtualization.
-
Compatibility with Cloud APIs:
- Cloud hypervisors adhere to cloud computing standards and are compatible with cloud application programming interfaces (APIs). This ensures interoperability with various cloud services and platforms.
Examples of cloud hypervisors include:
-
KVM (Kernel-based Virtual Machine): KVM is a Type 1 hypervisor that is widely used in cloud environments and is often integrated with virtualization management tools.
-
XenServer: XenServer is a virtualization platform based on the Xen hypervisor and is commonly used in cloud deployments.
-
VMware vSphere: VMware's vSphere suite includes a cloud hypervisor component for managing virtualized infrastructure in private and hybrid cloud environments.
Cloud hypervisors are a critical component in the infrastructure-as-a-service (IaaS) layer of cloud computing, providing the foundation for the virtualization and management of resources in the cloud.
Thank you.
