The Implications of Data Encryption for MIS
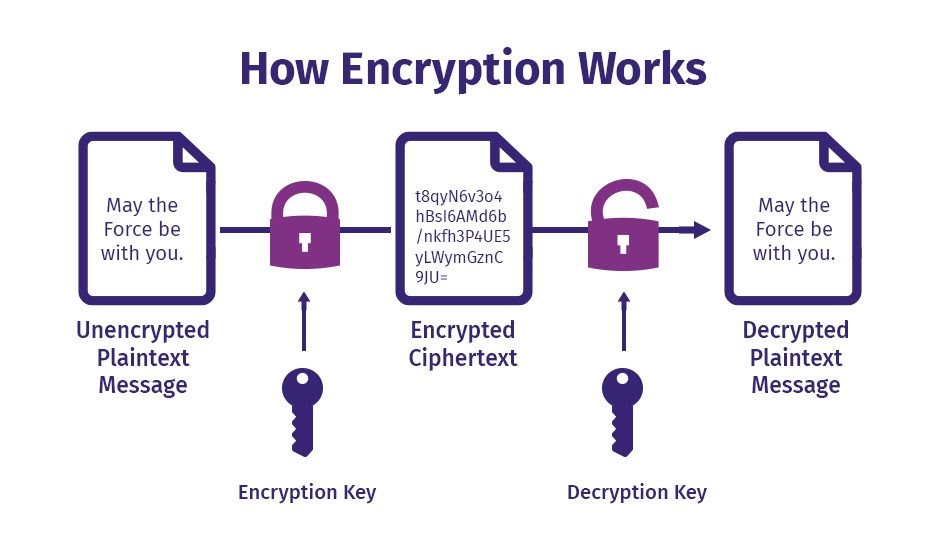
Data encryption has several implications for Management Information Systems (MIS):
Data Security: Encryption helps protect sensitive data stored within MIS systems from unauthorized access and data breaches. By encrypting data at rest and in transit, MIS systems ensure that even if attackers gain access to the underlying storage or communication channels, the encrypted data remains unintelligible and unusable without the appropriate decryption keys.
Compliance Requirements: Many regulatory frameworks and industry standards require organizations to encrypt sensitive data to protect confidentiality and ensure compliance with data protection regulations. Implementing encryption in MIS helps organizations meet these compliance requirements and avoid potential penalties or legal liabilities associated with data breaches or non-compliance.
Risk Mitigation: Encryption mitigates the risk of data exposure and loss by rendering data unreadable to unauthorized parties. This reduces the likelihood and impact of data breaches, insider threats, or unauthorized access attempts, thereby enhancing the overall security posture of MIS systems and the organization as a whole.
Protection of Confidential Information: MIS often store confidential information such as customer data, financial records, intellectual property, and trade secrets. Encryption safeguards this sensitive information from unauthorized disclosure or misuse, preserving the confidentiality and trustworthiness of the data within the MIS environment.
Data Integrity: Encryption techniques such as digital signatures and cryptographic hashes can be used to ensure data integrity within MIS systems. By digitally signing data or hashing it before encryption, MIS can verify the authenticity and integrity of the data during transmission or storage, detecting any unauthorized modifications or tampering attempts.
Secure Data Sharing: Encryption enables secure data sharing and collaboration within and outside the organization. MIS can encrypt data before sharing it with external partners, customers, or stakeholders, ensuring that only authorized recipients can access and decrypt the data. This facilitates secure data exchange while maintaining confidentiality and privacy.
Key Management: Effective encryption in MIS requires robust key management practices to securely generate, store, distribute, and revoke encryption keys. Key management systems help ensure the confidentiality and integrity of encryption keys, preventing unauthorized access or misuse of sensitive data.
Performance Considerations: Encryption introduces computational overhead and may impact the performance of MIS systems, particularly during data encryption and decryption operations. To mitigate performance impacts, MIS should employ efficient encryption algorithms, hardware acceleration, and optimized encryption protocols without compromising security.
User Authentication and Access Control: Encryption can be integrated with user authentication and access control mechanisms to enforce security policies and restrict access to encrypted data based on user privileges and permissions. This helps prevent unauthorized users or entities from accessing sensitive information within the MIS environment.
Overall, data encryption is essential for protecting sensitive information, ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements, mitigating security risks, maintaining data integrity, facilitating secure data sharing, managing encryption keys effectively, addressing performance considerations, and enhancing user authentication and access control within Management Information Systems.
Thank you,