Open-loop Control System
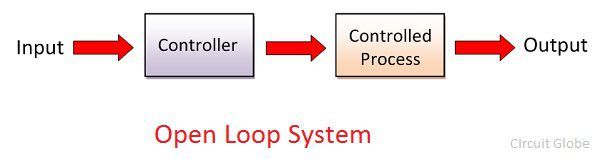
An open-loop control system, also known as a non-feedback control system, is a type of control system where the control action is not influenced by the system's output or feedback. In an open-loop control system, the control action is predetermined or pre-programmed based on the desired output or setpoint, without considering the actual output of the system.
Key characteristics of open-loop control systems include:
No Feedback Loop: Unlike closed-loop control systems, which use feedback from the system's output to adjust the control action, open-loop control systems do not incorporate feedback. The control action is determined solely based on the input or setpoint, without considering the system's actual response.
Fixed Control Action: In an open-loop control system, the control action is fixed or predetermined based on the desired output or setpoint. Once the control action is initiated, it continues unchanged regardless of any deviations or disturbances in the system.
Limited Adaptability: Open-loop control systems have limited adaptability to changes or variations in the system's behavior or external conditions. Since they do not adjust the control action based on feedback, they may not effectively compensate for disturbances, uncertainties, or nonlinearities in the system.
Simple Design: Open-loop control systems are often simpler in design compared to closed-loop control systems since they do not require feedback sensors or mechanisms for comparing the system's output to the desired setpoint. This simplicity can lead to lower cost and easier implementation in some applications.
Examples of open-loop control systems include:
While open-loop control systems are simple and cost-effective for certain applications, they may not provide accurate or reliable control in situations where the system dynamics are variable or unpredictable. Closed-loop control systems, which use feedback to adjust the control action based on the system's output, are often preferred for applications requiring greater accuracy, stability, and adaptability to changing conditions.
Thank you,