Concept and Classification of Hardware and Software
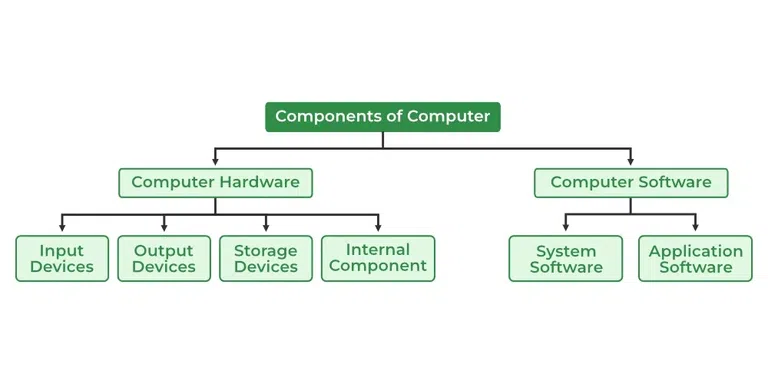
Hardware:
In the context of computing, hardware refers to the physical components or tangible parts of a computer system that can be seen and touched. These components work together to enable the functioning of a computer. Hardware includes devices and peripherals that process, store, and display data.

Some examples of computer hardware components are:
Central Processing Unit (CPU):
The CPU is the main processing unit of the computer responsible for executing instructions and performing calculations.
Motherboard:
The motherboard is the main circuit board that connects and allows communication between various hardware components.
Random Access Memory (RAM):
RAM is a type of memory used for temporary storage of data and instructions that the CPU can quickly access.
Hard Disk Drive (HDD) or Solid State Drive (SSD):
These are storage devices used for long-term data storage, such as operating systems, applications, and user files.
Graphics Processing Unit (GPU):
The GPU is responsible for rendering graphics and images, often used in gaming and graphics-intensive applications.
Monitor:
The monitor is an output device that displays visual information from the computer.
Keyboard and Mouse:
Input devices that allow users to interact with the computer and provide data and commands.
Printers and Scanners:
Output and input devices, respectively, used to produce hard copies of digital content and convert physical documents into digital data.
Software:
Software refers to the non-tangible programs and data that control and interact with the hardware to perform specific tasks on a computer. Unlike hardware, software cannot be physically touched but is essential for the operation and functionality of a computer system.
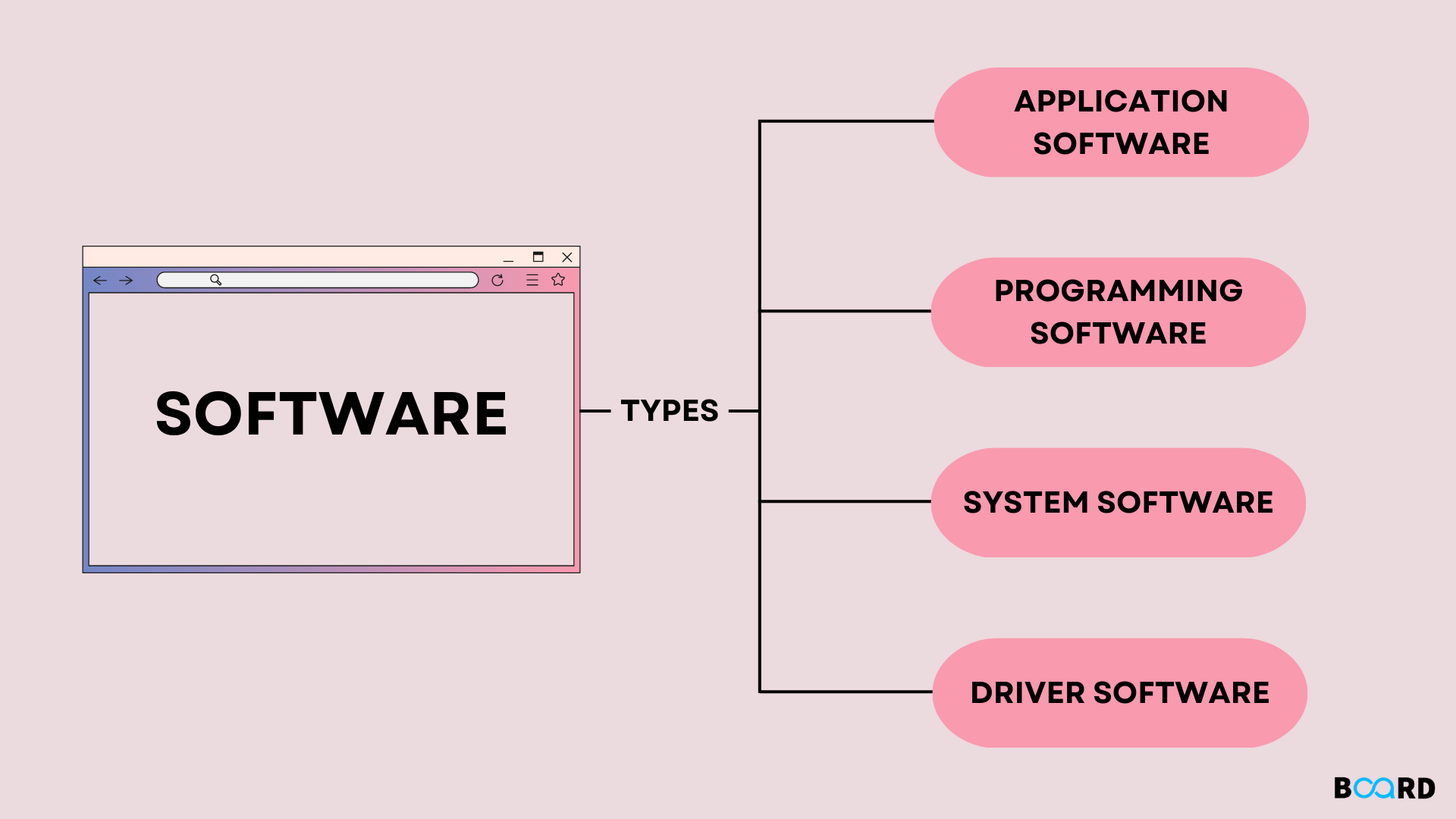
There are Two main Types of Software:
System Software:
System software manages computer hardware and provides a platform for running applications.
Key Components of System Software Include:
Operating System (OS):
The primary software that manages computer resources and provides a user interface for interaction.
Device Drivers:
Software that enables communication between the operating system and specific hardware devices.
Utilities:
Programs that perform various system maintenance tasks, such as disk cleanup, antivirus scanning, and file management.
Application Software:
Application software comprises programs designed for specific tasks or applications.

Examples of Application Software Include:
Word Processors:
Software for creating and editing documents, like Microsoft Word.
Web Browsers:
Programs for accessing and browsing the internet, like Google Chrome or Mozilla Firefox.
Image Editors:
Software for editing and manipulating images, like Adobe Photoshop.
Video Players:
Applications for playing multimedia files, like VLC Media Player.
Gaming Software:
Software for running video games and interactive entertainment.
Classification of Hardware and Software:
The classification of hardware and software is based on their distinct characteristics and functions:
Classification of Hardware:
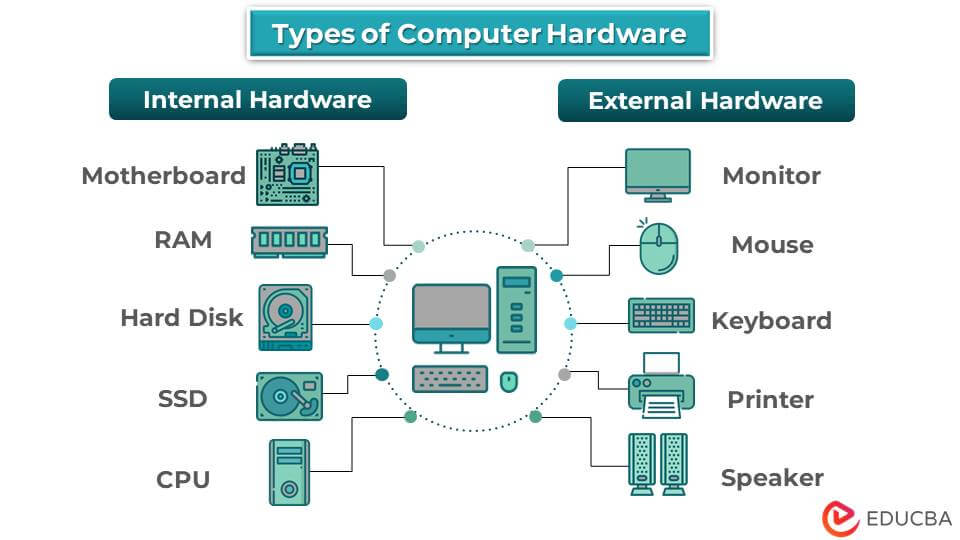
Internal Hardware:
Components installed inside the computer's casing, such as CPU, motherboard, RAM, and expansion cards.
External Hardware:
Devices connected to the computer externally, like monitors, keyboards, mice, printers, and scanners.
Input Devices:
Hardware that allows users to input data into the computer, such as keyboards, mice, and touchscreens.
Output Devices:
Hardware that displays or produces results from the computer, such as monitors, printers, and speakers.
Storage Devices:
Hardware used to store data, such as hard disk drives (HDDs) and solid-state drives (SSDs).
Processing Devices:
Refers specifically to the CPU, which executes instructions and processes data.
Classification of Software:

System Software:
Software that manages and controls the computer hardware, including the operating system, device drivers, and utilities.
Application Software:
Software designed for specific tasks or applications, such as word processors, web browsers, and multimedia players.
Operating System Type:
Software categorised by the operating system platform, such as Windows, macOS, Linux, or mobile operating systems (Android, iOS).
Licence Type:
Software classified based on its licensing model, such as open-source, freeware, shareware, or commercial software.
Purpose/Function:
Software categorised by its intended use, such as productivity software, graphics software, gaming software, etc.
Understanding the distinction between hardware and software is fundamental to comprehending how computers work and how different components contribute to the overall functionality of a computer system. Both hardware and software play crucial roles in enabling users to interact with computers, perform tasks, and utilise various applications for productivity, communication, entertainment, and more.
Thank You.