Flow Control
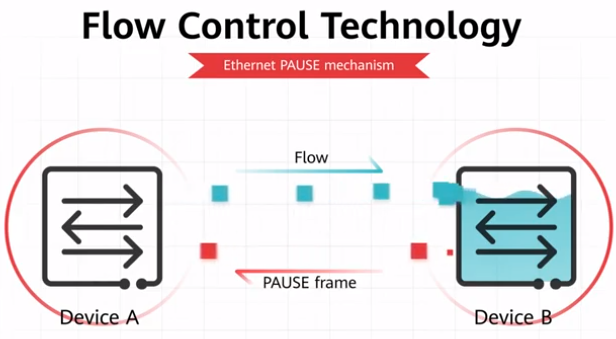
Flow control is a mechanism used in computer networks to manage the flow of data between two communicating devices, such as computers or networking equipment. Its purpose is to prevent data loss, minimize packet loss, and ensure efficient data transmission, especially in situations where the receiving device is unable to process incoming data as quickly as it is being sent by the transmitting device.
Flow control mechanisms help regulate the rate of data transmission to prevent congestion and avoid overwhelming the receiving device's buffer or memory. There are two primary types of flow control:
-
Buffer-based Flow Control:
- Buffer-based flow control, also known as buffering or store-and-forward flow control, involves the use of buffers or temporary storage areas in networking devices such as switches and routers.
- When a transmitting device sends data to a receiving device, the receiving device may temporarily store the data in its buffer if it is unable to process it immediately. The transmitting device is informed to pause or slow down transmission if the buffer becomes full, ensuring that data is not lost.
- This type of flow control is commonly used in Ethernet networks and other packet-switched networks.
-
Control-based Flow Control:
- Control-based flow control relies on explicit signals or messages exchanged between the transmitting and receiving devices to regulate the flow of data.
- One example of control-based flow control is the use of the Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) in the Internet Protocol (IP) suite. TCP uses a sliding window mechanism to manage the flow of data between sender and receiver.
- In TCP, the receiving device sends acknowledgment (ACK) packets to the transmitting device to indicate that data has been successfully received. The transmitting device adjusts its transmission rate based on the feedback received from the receiver, ensuring that data is transmitted at an optimal rate.
Flow control mechanisms help maintain the stability and efficiency of computer networks by preventing congestion, minimizing packet loss, and ensuring reliable data transmission. They play a crucial role in optimizing network performance, especially in situations where network bandwidth is limited or network resources are shared among multiple users or applications.
Thank you,