Chemical Classification of Matter
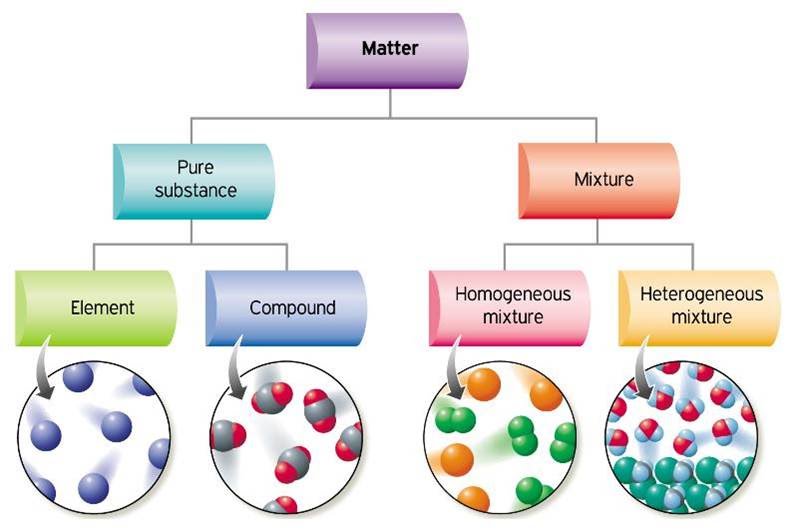
Chemical classification of matter categorizes substances based on their chemical composition and behavior during chemical reactions. Here are the main categories:
-
Elements: Elements are substances composed of only one type of atom. They cannot be broken down into simpler substances by chemical means. Each element is represented by a unique chemical symbol, such as H for hydrogen, O for oxygen, and Fe for iron.
-
Compounds: Compounds are substances composed of two or more different types of atoms chemically bonded together in fixed ratios. Compounds can be broken down into simpler substances (elements or other compounds) by chemical reactions. For example, water (H2O) is a compound composed of hydrogen and oxygen atoms bonded together.
-
Mixtures:
- Homogeneous Mixtures: Homogeneous mixtures have a uniform composition and properties throughout. They consist of two or more substances blended together at the molecular level, forming a single phase. Examples include solutions like saltwater and air.
- Heterogeneous Mixtures: Heterogeneous mixtures have a non-uniform composition, meaning they contain visibly distinct phases with different properties. Components of heterogeneous mixtures are not blended uniformly and can be separated by physical means. Examples include suspensions, colloids, and heterogeneous compounds.
-
Acids and Bases:
- Acids: Acids are substances that ionize in water to produce hydrogen ions (H+). They typically have a sour taste, turn blue litmus paper red, and react with metals to produce hydrogen gas. Examples include hydrochloric acid (HCl) and sulfuric acid (H2SO4).
- Bases: Bases are substances that ionize in water to produce hydroxide ions (OH-). They typically have a bitter taste, feel slippery, turn red litmus paper blue, and react with acids to form salts and water. Examples include sodium hydroxide (NaOH) and calcium hydroxide (Ca(OH)2).
-
Salts: Salts are ionic compounds formed by the reaction of an acid with a base. They consist of positively charged ions (cations) and negatively charged ions (anions) held together by electrostatic forces. Salts are often crystalline solids with high melting and boiling points. Examples include sodium chloride (NaCl) and calcium carbonate (CaCO3).
-
Organic and Inorganic Compounds:
- Organic Compounds: Organic compounds are compounds containing carbon atoms bonded to hydrogen atoms, along with other elements such as oxygen, nitrogen, sulfur, and halogens. They are typically associated with living organisms and exhibit a wide range of structures and functions. Examples include carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids.
- Inorganic Compounds: Inorganic compounds are compounds that do not contain carbon-hydrogen (C-H) bonds. They include minerals, metals, salts, and many other substances. Examples include sodium chloride (NaCl), calcium carbonate (CaCO3), and sulfuric acid (H2SO4).
Understanding the chemical classification of matter helps scientists and chemists organize and study the properties, behavior, and interactions of substances in various chemical systems and processes. It provides a framework for understanding the structure and function of matter at the molecular level.
Thank you,
