Classification of Matter
Matter can be classified into several categories based on its composition, physical state, and other properties. Here are the main classifications of matter:
-
Based on Composition:
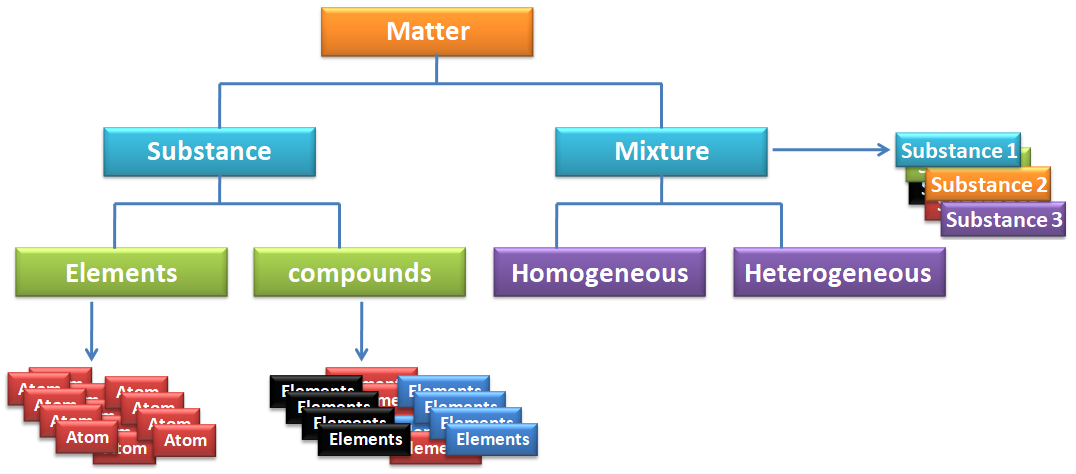
- Elements: Elements are substances that consist of only one type of atom. They cannot be broken down into simpler substances by chemical means. Examples include hydrogen, oxygen, carbon, and gold.
- Compounds: Compounds are substances composed of two or more different types of atoms chemically bonded together in fixed ratios. They can be broken down into simpler substances by chemical reactions. Examples include water (H2O), carbon dioxide (CO2), and sodium chloride (NaCl).
-
Based on Physical State:
- Solids: Solids have a definite shape and volume. The particles in solids are closely packed together and vibrate around fixed positions. Examples include ice, wood, and metal.
- Liquids: Liquids have a definite volume but take the shape of their container. The particles in liquids are close together but can move past one another, allowing liquids to flow. Examples include water, oil, and milk.
- Gases: Gases have neither a definite shape nor volume. The particles in gases are far apart and move freely, filling the entire volume of their container. Gases can expand to fill any space. Examples include air, oxygen, and carbon dioxide.
- Plasma: Plasma is a fourth state of matter that occurs at very high temperatures, where atoms are ionized, and electrons are stripped away, resulting in a mixture of positively charged ions and free electrons. Plasma is often found in stars, lightning, and certain types of flames.
-
Based on Homogeneity:
- Homogeneous: Homogeneous matter has uniform composition and properties throughout. It consists of a single phase, meaning it appears the same at the microscopic level. Examples include pure substances like elements and compounds, as well as homogeneous mixtures like solutions.
- Heterogeneous: Heterogeneous matter has non-uniform composition and properties, meaning it consists of multiple phases that are visibly distinct at the microscopic level. Examples include mixtures like suspensions, colloids, and heterogeneous compounds.
-
Based on Chemical Reactivity:
- Reactive Matter: Reactive matter refers to substances that readily undergo chemical reactions with other substances. They may react vigorously, produce heat, light, or other products. Examples include alkali metals (e.g., sodium) and certain organic compounds.
- Non-reactive Matter: Non-reactive matter refers to substances that are stable and do not readily undergo chemical reactions under normal conditions. Examples include noble gases (e.g., helium, neon) and inert substances like most metals.
Understanding the classification of matter helps scientists and engineers describe, analyze, and predict the behavior of substances in various contexts, from chemical reactions and material properties to environmental processes and industrial applications.
Thank you,
