How Does Obligation Work
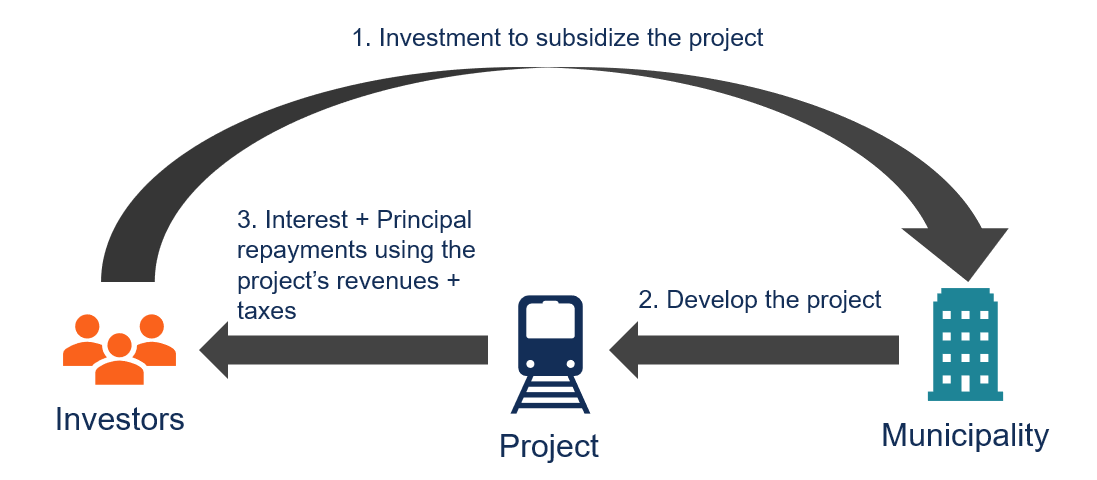
Obligations work by creating a sense of duty or responsibility that motivates individuals or entities to perform certain actions or fulfill specific duties. Here's how obligations typically work:
Identification: Obligations are typically recognized or established through various means, such as legal contracts, moral principles, social norms, or personal commitments. They may arise from formal agreements, laws, customs, expectations, or personal beliefs.
Understanding the Scope: Once an obligation is identified, individuals or entities need to understand the scope of what is required of them. This involves clarifying the nature of the obligation, its terms and conditions, any associated responsibilities, and the consequences of non-compliance.
Acceptance or Imposition: Obligations can be voluntarily accepted by individuals through agreements or contracts, as in the case of contractual obligations. Alternatively, obligations can be imposed on individuals by external authorities, such as legal obligations mandated by laws or regulations.
Performance: The next step is to fulfill the obligation by taking the necessary actions or carrying out the required tasks. This may involve providing goods or services, making payments, adhering to legal requirements, or acting in accordance with moral principles or social norms.
Compliance: Compliance with obligations involves meeting the specified requirements or standards within the agreed-upon timeframe. It often requires individuals to act responsibly, ethically, and in good faith to ensure that the obligations are fulfilled satisfactorily.
Consequences: Failure to fulfill obligations can have various consequences, depending on the nature and context of the obligation. Legal obligations may result in lawsuits, fines, or other legal sanctions for breach of contract or violation of laws. Moral obligations may lead to feelings of guilt, shame, or social disapproval for failing to uphold ethical principles or societal norms.
Reassessment: Obligations may be reassessed over time due to changes in circumstances, priorities, or legal requirements. Individuals and entities may need to renegotiate agreements, update contracts, or adjust their behaviors to accommodate new obligations or changes in existing ones.
Overall, obligations play a fundamental role in shaping human behavior, relationships, and societal interactions by establishing standards of conduct, fostering trust and cooperation, and promoting accountability and responsibility. Understanding and fulfilling obligations effectively are essential for maintaining harmony, fairness, and integrity in personal, professional, and social contexts.
Thank you,