The key Components of an Incremental Backup Strategy
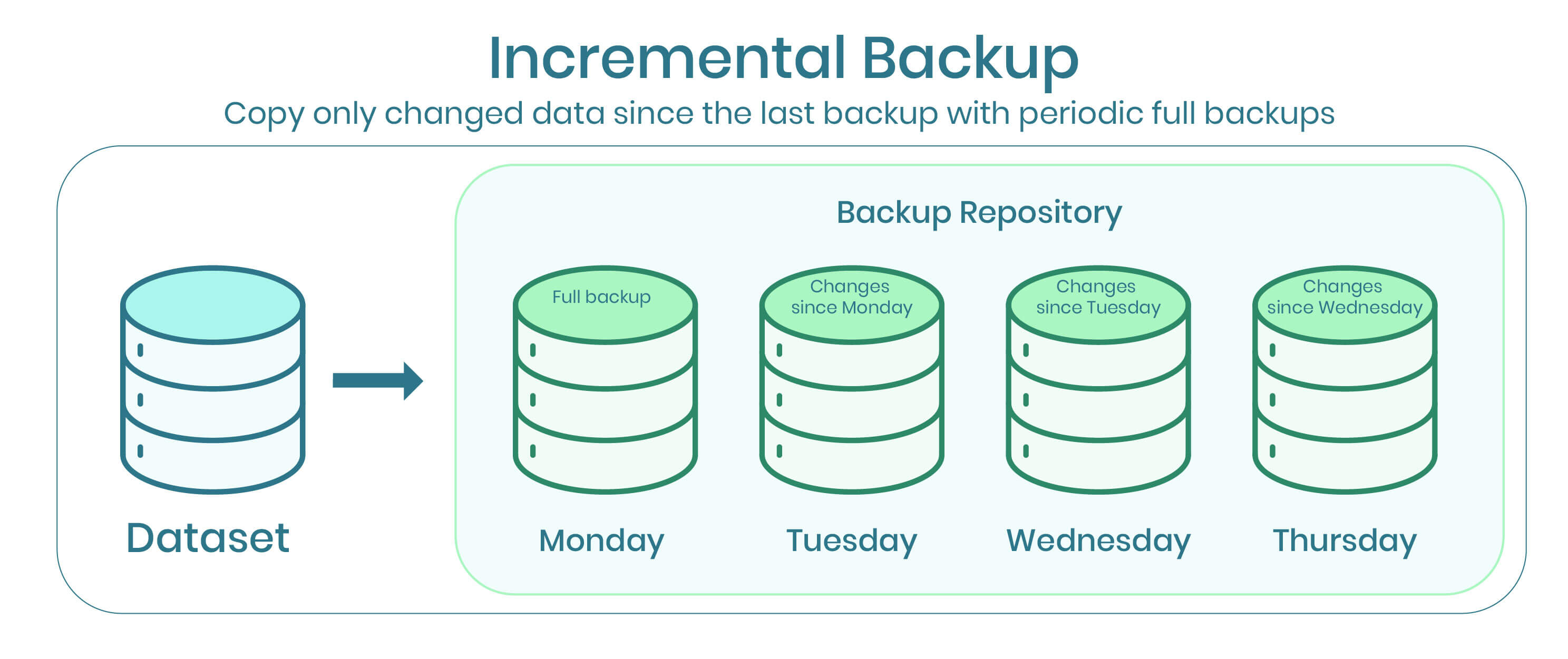
The key components of an incremental backup strategy include:
Full Initial Backup: The first step in an incremental backup strategy is to perform a full backup of all the selected data. This initial backup creates a baseline copy of the data from which subsequent incremental backups will be made.
Incremental Backups: After the full initial backup, incremental backups capture only the changes made to the data since the last backup operation. These changes can include newly created files, modified files, or deleted files. Incremental backups are typically performed at regular intervals, such as daily or hourly, depending on the organization's backup requirements.
Backup Schedule: An incremental backup strategy includes a defined backup schedule that determines when incremental backups are performed. The schedule should consider factors such as the frequency of data changes, backup window availability, and organizational recovery objectives.
Retention Policy: A retention policy dictates how long incremental backups are retained before they are replaced or removed from the backup storage. This policy should align with the organization's data retention requirements, compliance regulations, and recovery objectives. It ensures that backup storage resources are used efficiently while maintaining sufficient backup history for recovery purposes.
Full Backup Periodicity: While incremental backups capture changes since the last backup, periodic full backups are still necessary to create a complete snapshot of the data and ensure data integrity. The frequency of full backups may vary depending on factors such as data volatility, backup storage capacity, and recovery point objectives.
Backup Verification: Regular verification of incremental backups is essential to ensure data integrity and reliability. This verification process involves validating the integrity of backup files, verifying backup completeness, and testing the restore process to ensure that data can be successfully recovered when needed.
Offsite Backup Storage: To mitigate the risk of data loss due to disasters or physical damage to backup infrastructure, incremental backups should be stored offsite in a secure location. Offsite backup storage provides an additional layer of protection against data loss and ensures business continuity in the event of a catastrophic event.
By incorporating these key components into an incremental backup strategy, organizations can effectively protect their data, optimize backup operations, and facilitate efficient data recovery processes.
Thank you,