The Steps Involved in Building and Analyzing Simulation Models
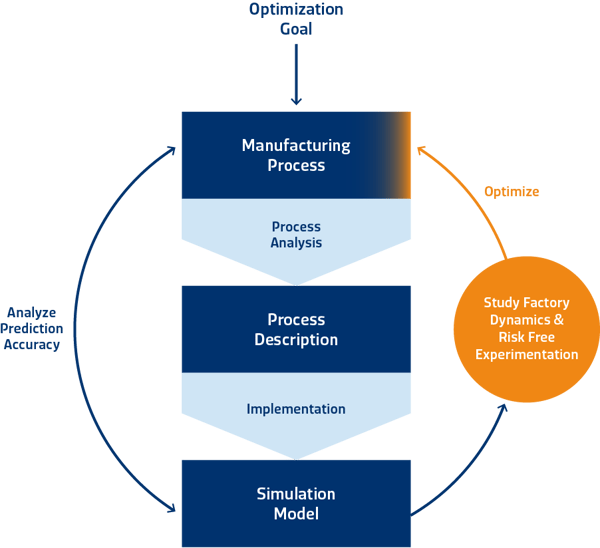
Building and analyzing simulation models involve several steps to effectively model, simulate, and analyze the behavior of complex systems. Here are the key steps involved in building and analyzing simulation models:
Problem Formulation: Clearly define the objectives of the simulation study and the problem to be addressed. Identify the system to be modeled, the entities involved, and the processes or interactions to be simulated. Establish the scope, assumptions, and constraints of the simulation study.
Conceptual Modeling: Develop a conceptual model of the system to be simulated. Identify the key components, entities, and interactions within the system. Define the states, events, and behaviors of the entities and processes. Determine the level of detail and abstraction required to capture the essential characteristics of the system.
Model Design: Design the simulation model based on the conceptual model. Choose an appropriate modeling approach, such as discrete-event simulation, agent-based simulation, or system dynamics. Select modeling elements, such as entities, resources, queues, and activities, to represent the components and processes of the system. Define input parameters, variables, and parameters that influence the behavior of the model.
Implementation: Implement the simulation model using simulation software or programming languages. Translate the conceptual model into computer code or simulation objects. Define the logic and rules governing the behavior of the entities, processes, and interactions in the model. Incorporate random variability, event scheduling, and other dynamic elements into the simulation logic.
Verification: Verify the correctness of the simulation model by ensuring that it accurately represents the intended system behavior. Validate the model against historical data, empirical observations, or analytical solutions, if available. Conduct unit testing, code review, and sensitivity analysis to identify and correct errors or inconsistencies in the model.
Validation: Validate the simulation model by comparing its behavior and outputs against real-world observations or expectations. Verify that the model accurately reproduces the dynamic behavior, trends, and patterns observed in the real system. Validate the model under different scenarios, input conditions, and boundary conditions to assess its robustness and reliability.
Experimentation: Conduct simulation experiments to analyze the behavior of the model and evaluate different scenarios, policies, or decision alternatives. Define experimental designs, input parameter settings, and performance metrics to be measured. Execute the simulation experiments, collect data on model outputs, and analyze the results to draw conclusions and insights.
Sensitivity Analysis: Perform sensitivity analysis to assess the sensitivity of model outputs to changes in input parameters, assumptions, or system conditions. Identify the most influential factors driving model behavior and uncertainty. Evaluate the impact of parameter variations on key performance metrics and decision outcomes.
Optimization: Apply optimization techniques to identify optimal solutions, policies, or decision rules based on simulation results. Use optimization algorithms, heuristic methods, or simulation-based optimization approaches to search for solutions that maximize performance, minimize costs, or achieve other objectives.
Documentation and Reporting: Document the simulation model, experimental setup, and analysis results in a comprehensive report or documentation. Describe the model structure, assumptions, input parameters, and validation procedures. Present the simulation experiments, results, and findings in a clear, concise manner. Communicate insights, conclusions, and recommendations to stakeholders and decision-makers.
By following these steps, simulation modelers can effectively build, analyze, and utilize simulation models to gain insights into complex systems, evaluate decision alternatives, and improve decision-making processes.
Thank you,