Payment gateways work in E-Commerce
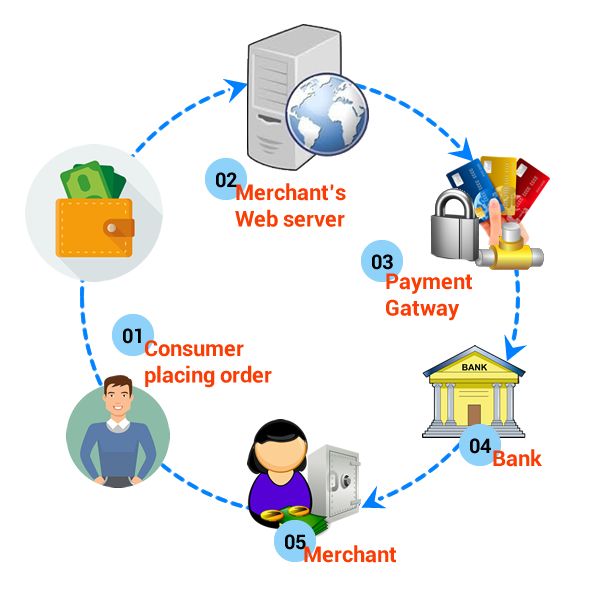
Payment gateways play a crucial role in facilitating secure online transactions in e-commerce. Here's how they work:
Customer Places an Order: The e-commerce transaction begins when a customer adds products to their shopping cart and proceeds to checkout on the merchant's website or platform.
Payment Information Entered: At checkout, the customer provides their payment information, such as credit card details, billing address, and contact information. This information is entered into the payment form on the e-commerce website.
Payment Data Encryption: To ensure the security of sensitive payment information, the payment gateway encrypts the data using secure socket layer (SSL) encryption or transport layer security (TLS) encryption. This encryption process scrambles the data, making it unreadable to unauthorized parties during transmission over the internet.
Transmission to Payment Gateway: Once the payment information is entered and encrypted, the e-commerce website sends the data to the selected payment gateway for processing. The payment gateway acts as an intermediary between the merchant's website and the payment processor.
Authorization Request: The payment gateway forwards the encrypted payment data to the payment processor or acquiring bank for authorization. The payment processor then communicates with the customer's bank or card issuer to verify the transaction details and ensure that there are sufficient funds available for the purchase.
Authorization Response: Upon receiving the authorization request, the customer's bank or card issuer evaluates the transaction and sends an authorization response back to the payment processor through the payment gateway. The response indicates whether the transaction is approved or declined.
Transaction Processing: If the transaction is approved, the payment processor sends an authorization code to the payment gateway, indicating that the payment has been authorized. The payment gateway relays this information to the e-commerce website, allowing the transaction to proceed.
Confirmation and Order Fulfillment: Once the payment is authorized, the e-commerce website confirms the order and initiates the order fulfillment process. The customer receives a confirmation email or notification, and the merchant proceeds to fulfill the order by shipping the products or providing access to digital goods or services.
Settlement and Funds Transfer: After the transaction is completed, the payment processor settles the funds by transferring the authorized amount from the customer's bank to the merchant's account. This settlement process typically occurs within a few business days, depending on the payment processor and bank policies.
Transaction Recordkeeping: Both the payment gateway and the e-commerce website maintain transaction records for accounting, reconciliation, and dispute resolution purposes. These records include details such as transaction ID, timestamp, amount, payment method, and customer information.
Overall, payment gateways provide a secure and seamless way for e-commerce businesses to accept online payments, ensuring that transactions are processed efficiently and securely while protecting sensitive customer data.
Thank you,