Difference between Heart Attack and Cardiac Arrest
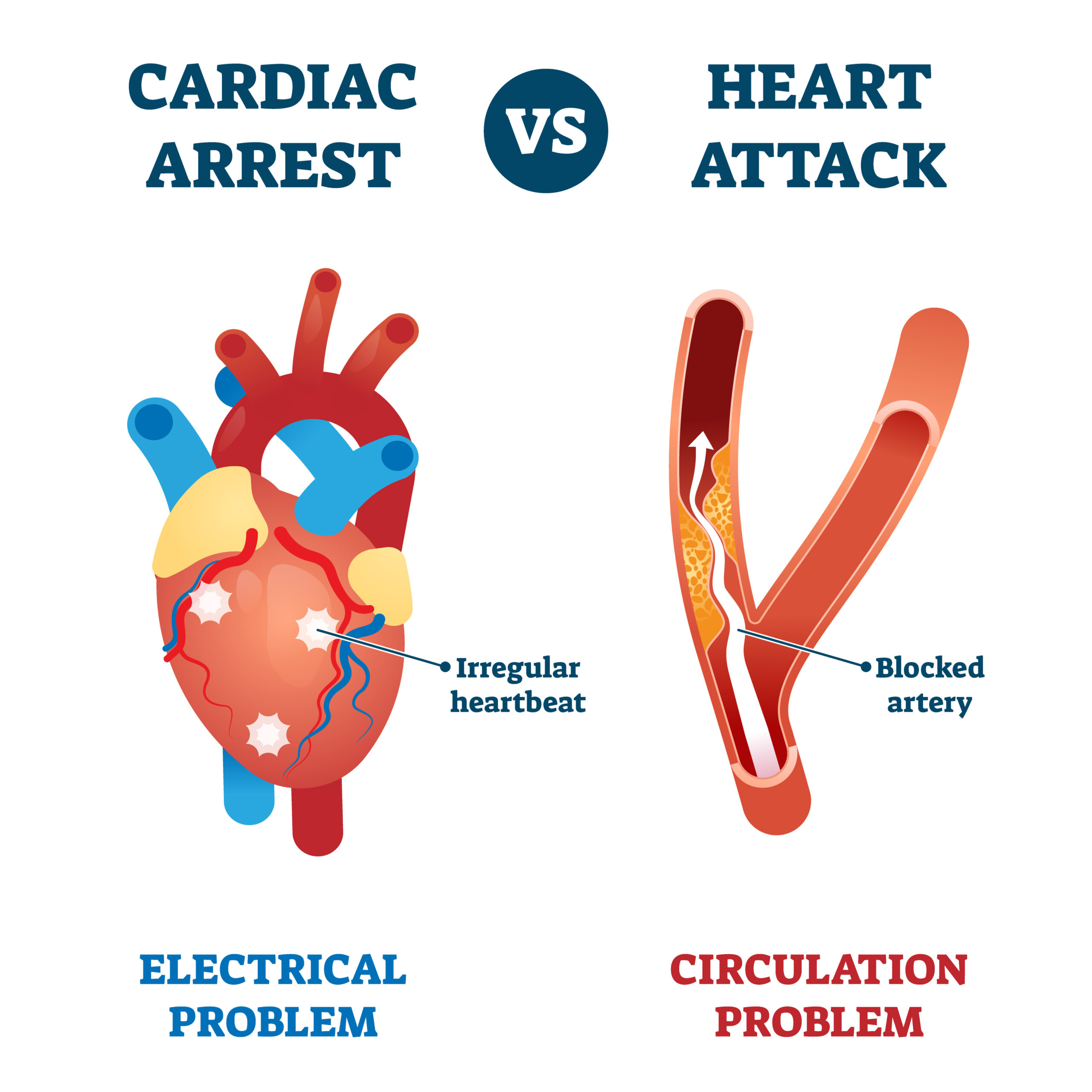
Heart attack and cardiac arrest are both serious medical emergencies involving the heart, but they are distinct conditions with different causes, symptoms, and treatments. Here are the key differences between a heart attack and cardiac arrest:
-
Cause:
- Heart Attack (Myocardial Infarction): A heart attack occurs when blood flow to a part of the heart muscle is blocked, usually due to the buildup of plaque (atherosclerosis) in the coronary arteries. This blockage deprives the heart muscle of oxygen and nutrients, leading to tissue damage or death.
- Cardiac Arrest: Cardiac arrest occurs when the heart suddenly stops beating effectively, leading to a cessation of blood flow to the body and vital organs. Cardiac arrest is typically caused by an electrical disturbance in the heart's rhythm, such as ventricular fibrillation or ventricular tachycardia.
-
Symptoms:
- Heart Attack: Common symptoms of a heart attack include chest pain or discomfort (often described as pressure, tightness, or squeezing), pain or discomfort in other upper body areas (such as the arms, back, neck, jaw, or stomach), shortness of breath, nausea, vomiting, cold sweats, fatigue, and anxiety. Symptoms of a heart attack can vary and may differ between men and women.
- Cardiac Arrest: Cardiac arrest often occurs suddenly and without warning. The person may suddenly collapse, lose consciousness, stop breathing, and have no pulse. There may be no warning signs or symptoms before cardiac arrest occurs.
-
Treatment:
- Heart Attack: Treatment for a heart attack often involves quickly restoring blood flow to the blocked artery to prevent further damage to the heart muscle. This may involve medications (such as aspirin, nitroglycerin, and clot-busting drugs) and procedures to open the blocked artery, such as angioplasty and stent placement or coronary artery bypass surgery.
- Cardiac Arrest: Treatment for cardiac arrest involves immediate cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) to manually circulate blood and deliver oxygen to vital organs. Early defibrillation with an automated external defibrillator (AED) to restore a normal heart rhythm is also crucial. Advanced cardiac life support (ACLS) provided by trained medical professionals may include medications, advanced airway management, and other interventions to support circulation and restore heart function.
-
Outcome:
- Heart Attack: With prompt medical treatment, many people survive heart attacks and go on to recover, although some may experience long-term complications or require ongoing treatment for heart disease.
- Cardiac Arrest: Cardiac arrest is a medical emergency with a high risk of death if not treated immediately. Survival depends on prompt recognition of symptoms, early access to emergency medical care, and immediate initiation of CPR and defibrillation.
In summary, while heart attacks and cardiac arrest both involve the heart and are serious medical emergencies, they have different causes, symptoms, and treatments. It's important to understand the distinctions between these conditions and know how to respond appropriately in each situation. Prompt recognition of symptoms and access to emergency medical care are critical for improving outcomes in cases of heart attack and cardiac arrest.
Thank you,
