Key differences between the Broadcast and Multicast
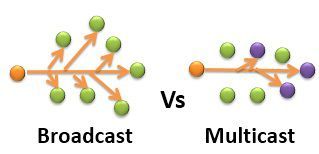
Broadcast and multicast are both communication methods used in networking, but they differ in their target audience and how data is transmitted. Here are the key differences between broadcast and multicast:
-
Target Audience:
- Broadcast: In a broadcast communication, data is sent from one sender to all devices on the network. Every device on the network receives the data, regardless of whether it needs or wants it.
- Multicast: In multicast communication, data is sent from one sender to a specific group of recipients who have expressed interest in receiving the data. Only devices that have subscribed to the multicast group receive the data.
-
Efficiency:
- Broadcast: Broadcast communication can be inefficient because it sends data to every device on the network, including devices that may not need the data. This can lead to unnecessary network traffic and waste bandwidth.
- Multicast: Multicast communication is more efficient because it sends data only to devices that have joined the multicast group and have expressed interest in receiving the data. This conserves bandwidth and reduces network congestion.
-
Scalability:
- Broadcast: Broadcast communication does not scale well, especially in large networks, because it sends data to every device indiscriminately. As the network grows, the amount of network traffic generated by broadcast communication increases significantly.
- Multicast: Multicast communication scales much better than broadcast because it sends data only to devices that have joined the multicast group. As the network grows, multicast traffic remains limited to the devices that are part of the multicast group, resulting in more efficient use of network resources.
-
Routing:
- Broadcast: Broadcast traffic is typically handled by network devices such as routers and switches, which must forward the data to every device on the network. This can put a strain on network infrastructure, especially in large networks.
- Multicast: Multicast traffic is also handled by network devices, but it is more efficiently routed using multicast routing protocols. These protocols ensure that multicast data is only forwarded to devices that have joined the multicast group, reducing unnecessary network traffic.
In summary, the key difference between broadcast and multicast lies in their target audience and efficiency. Broadcast sends data to every device on the network, while multicast sends data only to devices that have joined a specific multicast group. Multicast is more efficient and scalable than broadcast, making it a preferred choice for applications that require one-to-many communication over IP networks.
Thank you,
