Block Cipher
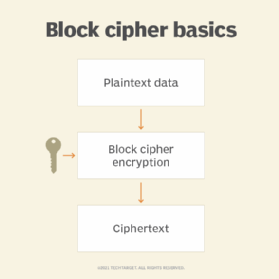
A block cipher is a cryptographic algorithm that operates on fixed-length groups of bits, called blocks, to encrypt or decrypt plaintext data. These algorithms take a block of plaintext and transform it into a block of ciphertext using a key. The same key is used for both encryption and decryption, making block ciphers symmetric-key algorithms.
In a block cipher, the input plaintext block and the key are combined through a series of mathematical operations, typically substitution and permutation, to produce the corresponding ciphertext block. The size of the input block and the key length are fixed and defined by the specific block cipher algorithm.
The primary characteristics of block ciphers include:
Block Size: The size of the input and output blocks, which is typically fixed for a given cipher. Common block sizes include 64 bits (as in DES), 128 bits (as in AES), or 256 bits (as in some AES variants).
Key Size: The length of the key used for encryption and decryption. The key size determines the strength of the encryption and is an important factor in resisting cryptographic attacks.
Encryption and Decryption: Block ciphers have algorithms for both encryption and decryption. The encryption algorithm transforms plaintext into ciphertext, while the decryption algorithm reverses this process to recover the original plaintext.
Mode of Operation: Block ciphers are often used in combination with modes of operation to encrypt data of arbitrary length. Common modes include Electronic Codebook (ECB), Cipher Block Chaining (CBC), Counter (CTR), and Galois/Counter Mode (GCM).
Security: The security of a block cipher depends on factors such as the key size, the design of the algorithm, and its resistance to various cryptographic attacks, including brute-force attacks, differential cryptanalysis, and linear cryptanalysis.
Examples of well-known block ciphers include the Data Encryption Standard (DES), Advanced Encryption Standard (AES), and Blowfish. Block ciphers are widely used in various cryptographic applications, including securing communication over networks, protecting stored data, and ensuring the confidentiality and integrity of sensitive information.
Thank you,