Phases of Penetration Testing
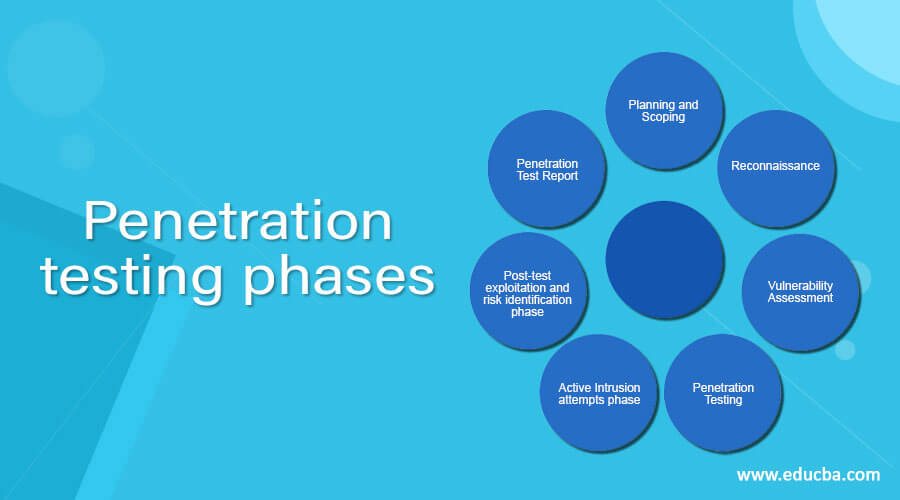
Penetration testing typically follows a structured approach with distinct phases to ensure a comprehensive evaluation of an organization's security. The common phases of penetration testing include:
-
Pre-engagement:
- Scope Definition: Clearly define the scope of the penetration test, including the systems, networks, applications, and specific testing goals.
- Rules of Engagement: Establish rules and limitations for the testing, including what actions are allowed and any constraints on the testing team.
-
Information Gathering (Reconnaissance):
- Passive Reconnaissance: Collect information about the target without directly interacting with it, such as through publicly available information, social media, and domain registration details.
- Active Reconnaissance: Actively scan the target's network to gather more detailed information, including IP addresses, open ports, and services.
-
Threat Modeling:
- Identify potential threats and vulnerabilities based on the information gathered. This helps prioritize testing efforts and focus on areas most likely to be targeted by attackers.
-
Vulnerability Analysis:
- Use automated tools and manual techniques to identify and assess vulnerabilities in the target systems, applications, and networks.
- Prioritize vulnerabilities based on their severity and potential impact.
-
Exploitation:
- Attempt to exploit identified vulnerabilities to gain unauthorized access or perform other malicious actions.
- Validate the impact of successful exploits on the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of the system.
-
Post-Exploitation:
- Explore the compromised system to understand the extent of access gained.
- Document the steps taken and potential avenues for further exploitation or lateral movement within the network.
-
Analysis and Reporting:
- Compile and analyze the findings from the penetration test.
- Create a detailed report that includes an executive summary, a description of the testing process, identified vulnerabilities, their severity, and recommendations for remediation.
-
Cleanup and Restitution:
- Ensure that any changes made during the penetration test are reverted to their original state.
- Address any unintended consequences or disruptions caused during testing.
-
Communication:
- Present the findings to the stakeholders, including management, IT teams, and other relevant personnel.
- Discuss the implications of the findings, potential risks, and recommended remediation steps.
-
Re-Testing:
- After the organization addresses the identified vulnerabilities and implements remediation measures, conduct a follow-up penetration test to verify that the issues have been effectively addressed.
- Re-testing ensures that the security improvements are successful and that new vulnerabilities have not been introduced.
-
Documentation:
- Maintain detailed documentation of the entire penetration testing process, including the methodologies used, tools employed, findings, and remediation actions taken.
It's important to note that the penetration testing process requires collaboration between the testing team and the organization's stakeholders. Clear communication, well-defined scopes, and a focus on continuous improvement contribute to the effectiveness of penetration testing in enhancing an organization's security posture.
Thank You.
