Hardness is a material property that describes its resistance to deformation, scratching, or penetration. There are various types of hardness tests and scales used to quantify this property, each with its own methodology and purpose.
Here are some of the most common types of hardness:
Mohs Hardness: The Mohs scale of mineral hardness is a qualitative scale that ranks minerals based on their ability to scratch each other. It's primarily used in geology and mineralogy to compare the hardness of different minerals. The scale ranges from 1 (the softest, talc) to 10 (the hardest, diamond).
Brinell Hardness: This test involves pressing a hardened steel ball into the surface of a material and measuring the diameter of the impression. The Brinell hardness number is calculated based on the applied load and the diameter of the indentation. It's commonly used for testing materials with coarse microstructures or materials that are too rough for other hardness tests.
Rockwell Hardness: The Rockwell hardness test measures the depth of penetration of an indenter (either a diamond cone or a steel ball) into a material under a specific load. There are different scales within the Rockwell system, such as the Rockwell A, B, C, and D scales, each suited for different types of materials and indentation depths.
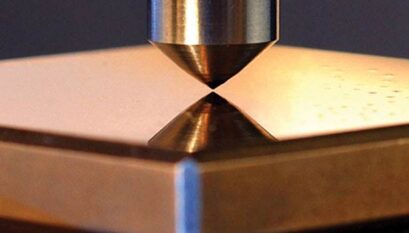
Vickers Hardness: In the Vickers hardness test, a diamond indenter is used to create a square-based pyramid indentation. The diagonals of the indentation are measured, and the Vickers hardness number is calculated based on the applied load and the area of the indentation. It's suitable for a wide range of materials and provides a precise measurement.
Knoop Hardness: Similar to the Vickers test, the Knoop hardness test uses a pyramidal diamond indenter, but the indenter's geometry is different, resulting in a more elongated indentation. This test is often used for brittle materials and thin coatings.
Shore Hardness: Shore hardness measures the resistance of polymers and elastomers to indentation. There are different scales within the Shore hardness test, such as Shore A, B, D, etc., each suitable for different types of materials.
Microhardness: Microhardness testing involves using a small indenter to measure the hardness of small or thin samples, often at a microscopic level. Vickers and Knoop tests are commonly used for microhardness testing.
Superficial Hardness: This is a variation of the Rockwell hardness test, where lower test forces and shallower indentations are used. It's useful for measuring the hardness of thin materials, surface layers, and case-hardened parts.
Each type of hardness test has its own advantages, limitations, and applications. The choice of test method depends on factors like the material being tested, the required precision, and the specific properties being evaluated.
Thank You