How Does Computer Work:
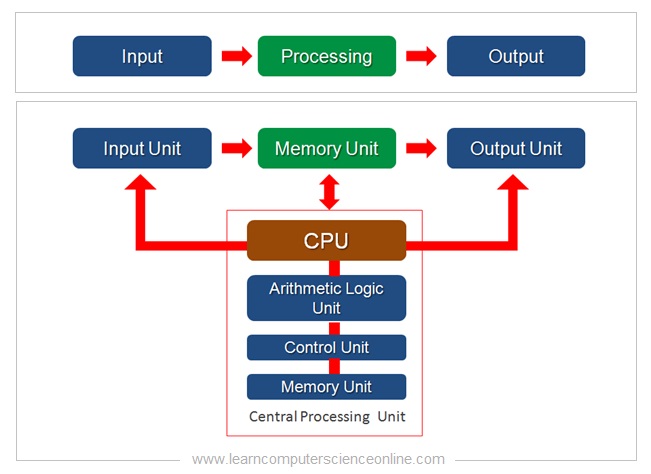
Understanding how a computer works involves delving into its key components and the process through which it executes instructions to perform tasks. Here's a simplified explanation of how a computer works:
Input:
The process begins with the computer receiving input from the user or external devices. Input devices, such as keyboards, mice, touchscreens, and microphones, allow users to provide data, commands, or interactions to the computer.
Processing:
The central processing unit (CPU) is the core of the computer and responsible for processing the input data. The CPU fetches instructions from memory and executes them, performing arithmetic and logical operations on the data as directed by the instructions.
Memory:
Data and instructions required for processing are stored temporarily in the computer's memory. Random Access Memory (RAM) is used as temporary storage during the computer's operation because it allows quick access to data. The CPU fetches data from memory, processes it, and stores the results back in memory.
Storage:
While RAM provides temporary storage, the computer also has long-term storage devices like hard drives, solid-state drives (SSDs), or other storage media. These devices retain data even when the computer is turned off and are used to store the operating system, software applications, files, and user data.
Processing Instructions:
The CPU reads and executes instructions from programs stored in memory. These programs are written in programming languages and converted into machine code (binary) that the CPU can understand and execute.
Arithmetic and Logic Unit (ALU):
The ALU is a part of the CPU responsible for performing arithmetic calculations (addition, subtraction, multiplication, division) and logical operations (comparisons, AND/OR operations) on data.
Control Unit:
The control unit of the CPU manages and coordinates the execution of instructions. It fetches instructions from memory, decodes them, and sends signals to other parts of the computer to carry out the necessary operations.
Output:
After processing the data, the computer produces output for the user or other devices. Output devices, such as monitors, printers, and speakers, display, print, or play the results of the computer's processing.
Feedback Loop:
Computers can receive continuous input and provide output in response to changes in the environment. This feedback loop allows them to interact with users and respond dynamically to changing conditions.
Operating System:
The operating system is a crucial piece of software that manages computer resources, provides a user interface, and facilitates communication between hardware and software components. It allows users to interact with the computer and manage files and applications effectively.
This basic overview illustrates how a computer's components work together to process data and perform tasks. The speed and efficiency of modern computers, along with their ability to handle complex tasks, are a result of advancements in hardware technology, software optimization, and improved algorithms. As computers continue to evolve, they become more powerful and enable us to explore new frontiers in various fields, making them an indispensable tool in today's world.
Thank You.