Key differences between OSPF and BGP Protocol
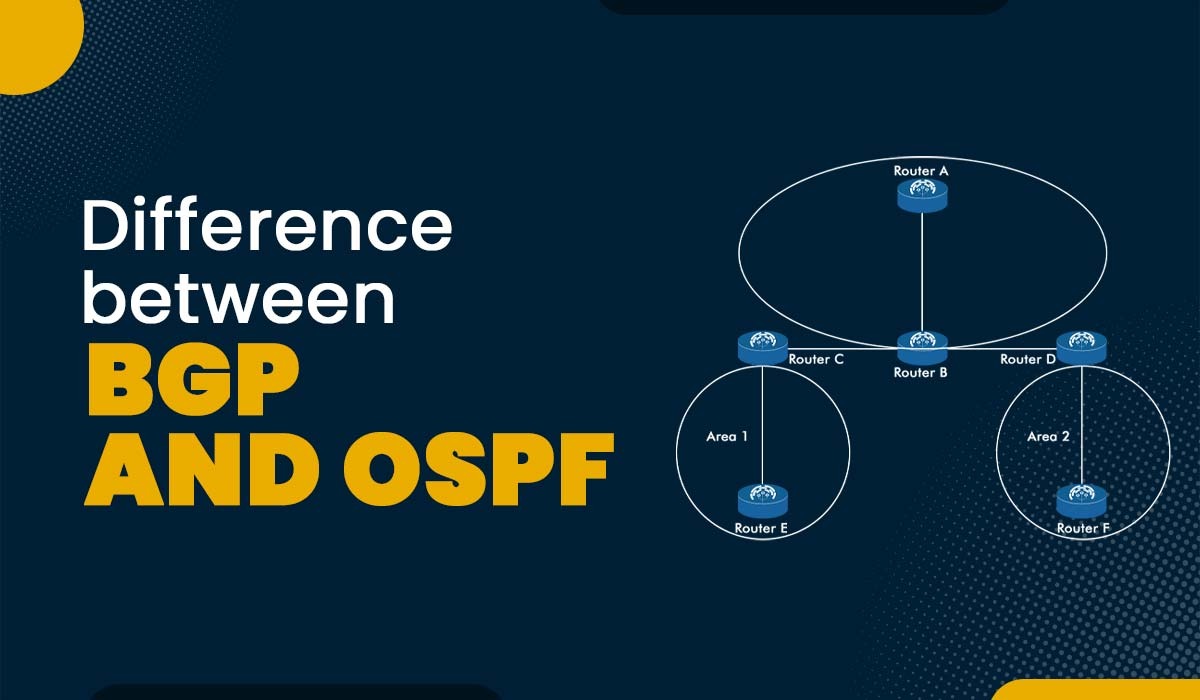
OSPF (Open Shortest Path First) and BGP (Border Gateway Protocol) are both routing protocols, but they serve different purposes and operate at different levels of the networking hierarchy. Here are key differences between OSPF and BGP:
-
Scope and Use:
- OSPF:
- Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP) used within an Autonomous System (AS).
- Typically used for routing within an enterprise network or a service provider's network.
- BGP:
- Exterior Gateway Protocol (EGP) used between Autonomous Systems (ASes).
- Designed for routing between different organizations, ISPs, or large-scale networks.
-
Topology:
- OSPF:
- Operates within a single AS and supports hierarchical design with areas.
- Uses a link-state database to represent the network topology.
- BGP:
- Operates between different ASes on the internet.
- Focuses on exchanging reachability information between different domains.
-
Path Vector vs. Link-State:
- OSPF:
- Link-state routing protocol.
- Maintains a detailed database of the network's link state to make routing decisions.
- BGP:
- Path vector routing protocol.
- Advertises paths and uses policy-based attributes to make routing decisions.
-
Convergence:
- OSPF:
- Generally converges faster than BGP.
- Uses link-state databases and a distributed SPF (Shortest Path First) algorithm for quick convergence.
- BGP:
- Slower convergence compared to OSPF.
- Designed for stability and slow adaptation to changes in the internet's global routing table.
-
Policy-Based Routing:
- OSPF:
- Supports limited policy-based routing.
- Policies are often simpler compared to BGP.
- BGP:
- Designed for extensive policy-based routing.
- Network administrators can define complex policies based on attributes like AS path, origin, and others.
-
Authentication:
- OSPF:
- Provides mechanisms for authenticating routing information exchanges within an AS.
- BGP:
- Supports authentication between routers belonging to different ASes.
-
Address Families:
- OSPF:
- Originally designed for IPv4, with later extensions to support IPv6.
- BGP:
- Supports both IPv4 and IPv6 address families.
-
Network Type:
- OSPF:
- Commonly used in enterprise networks, data centers, and service provider networks.
- BGP:
- Predominantly used for internet routing between different ASes.
-
Administrative Distances:
- OSPF:
- Typically has a lower administrative distance (AD) than BGP.
- BGP:
- Generally has a higher AD than OSPF, indicating a less preferred route within a router.
-
Neighbor Discovery:
- OSPF:
- Uses Hello packets for neighbor discovery within the same area.
- BGP:
- Establishes peering relationships using TCP connections, and neighbors are explicitly configured.
-
Hierarchical Design:
- OSPF:
- Hierarchical design is inherent, with areas to reduce the size of the link-state database.
- BGP:
- Does not have a hierarchical structure like OSPF, but relies on route aggregation and summarization.
Understanding these differences is crucial when designing and managing networks, as OSPF and BGP serve distinct roles and are optimized for different aspects of routing in the networking landscape.
Thank you,
