Phishing Work
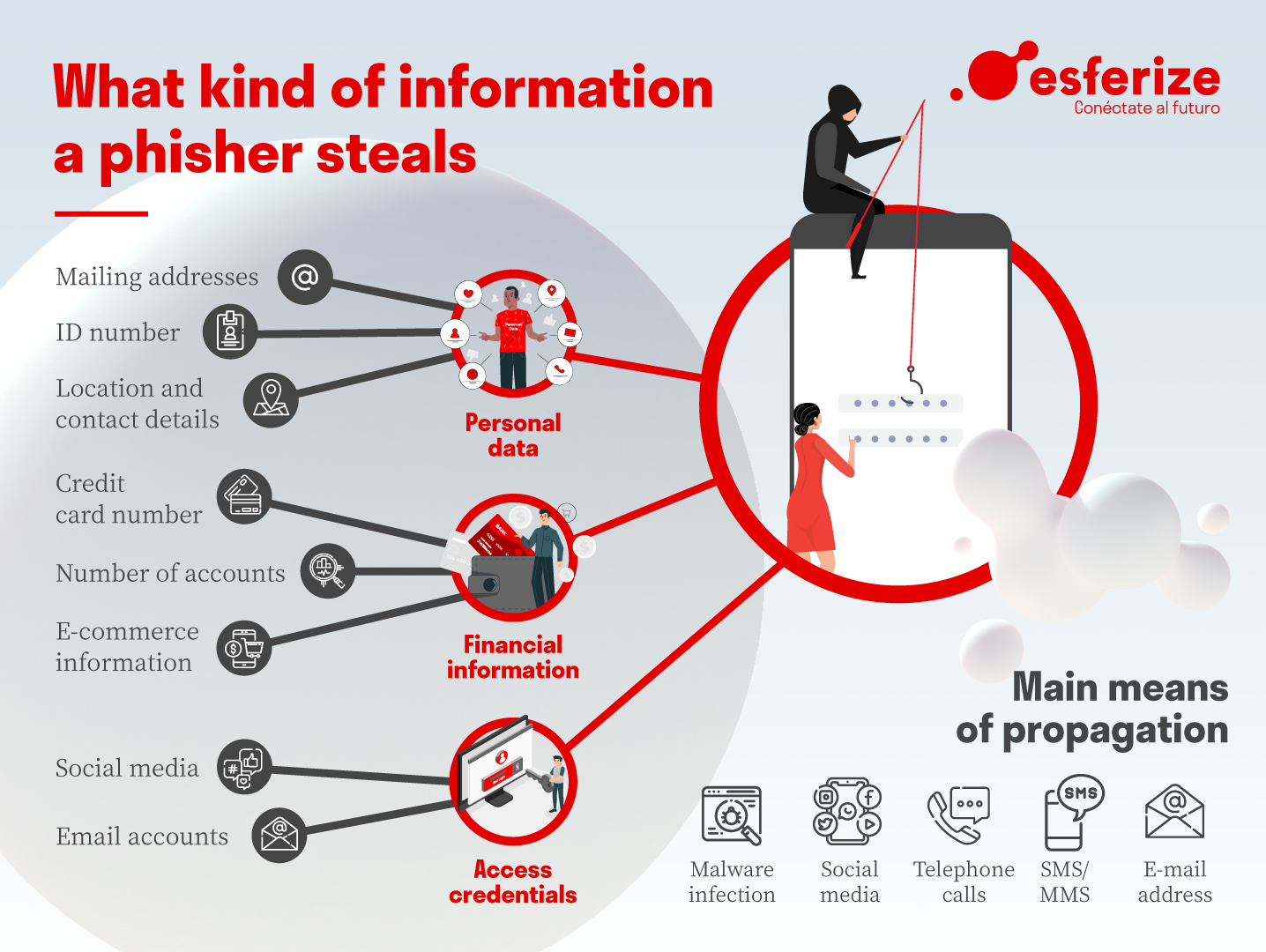
Phishing works by exploiting human psychology and trust to trick individuals into divulging sensitive information or taking actions that could compromise their security. Here's a general overview of how phishing typically works:
-
Baiting the Hook:
- Attackers choose a target or a group of targets, often based on characteristics like job roles, affiliations, or interests.
- They create a convincing and enticing message, usually in the form of an email, but it could also be a text message, social media post, or even a phone call.
-
Crafting a Deceptive Message:
- Phishing messages often mimic legitimate communication from trusted entities, such as banks, government agencies, or popular online services.
- The messages may use urgent language, threats, or offers that grab the recipient's attention and prompt them to take immediate action.
-
Using Spoofed Identities:
- Attackers often use techniques to make their messages appear legitimate. This includes using email addresses, logos, and language that closely resemble those of reputable organizations.
-
Inserting Malicious Links or Attachments:
- Phishing emails usually contain links to fake websites or malicious attachments. Clicking on these links or downloading attachments may install malware on the victim's device or lead them to a fraudulent website designed to capture sensitive information.
-
Exploiting Trust and Urgency:
- Phishing messages often create a sense of urgency or fear, encouraging recipients to act quickly without thinking critically. This urgency can lead individuals to overlook red flags.
-
Collecting Information:
- When recipients click on the provided links or enter information on fraudulent websites, attackers capture the sensitive data, such as usernames, passwords, credit card numbers, or personal details.
-
Concealing Their Tracks:
- After obtaining the desired information, attackers may use various techniques to cover their tracks, making it more challenging for security professionals to trace the phishing attack back to its source.
It's crucial for individuals to be vigilant and skeptical of unexpected or suspicious messages. Verifying the legitimacy of communications, avoiding clicking on unknown links, and using security measures like two-factor authentication can help protect against phishing attacks. Additionally, organizations often implement security awareness training and employ technologies to detect and prevent phishing attempts.
Thank you.
