Solar Cells Function at The Molecular Level
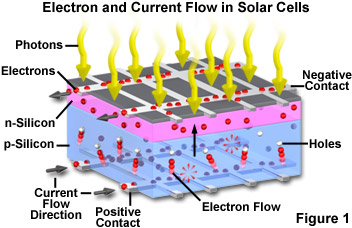
At the molecular level, solar cells function through a process called the photovoltaic effect, which involves the interaction between photons (particles of light) and semiconductor materials within the solar cell. Here's how solar cells work at the molecular level:
Generation of Electron-Hole Pairs: The absorbed photons excite electrons in the semiconductor material, causing them to break free from their atomic bonds and create electron-hole pairs. This process generates free electrons (negatively charged) and "holes" (positively charged vacancies) within the semiconductor material.
Separation of Charges: The electric field within the semiconductor material of the solar cell causes the free electrons to move towards the n-type (negative) side of the cell, while the holes move towards the p-type (positive) side. This separation of charges creates an electric potential difference, or voltage, across the solar cell.
Flow of Current: When an external circuit is connected to the solar cell, the separated charges can flow through the circuit as electric current. Electrons flow from the n-type side of the cell through the external circuit to the p-type side, creating a flow of electricity.
Generation of Electricity: As electrons flow through the external circuit, they can power electrical devices, such as lights, appliances, or electronic devices. This electricity can be used immediately or stored in batteries for later use.
Recombination: To maintain the flow of electricity, it's essential to prevent the recombination of electrons and holes within the semiconductor material. This can be achieved through various techniques, such as doping the semiconductor material with impurities, optimizing the design of the solar cell structure, and minimizing defects and imperfections in the material.
Continuous Process: The process of photon absorption, electron-hole pair generation, charge separation, and current flow occurs continuously as long as sunlight is available and the solar cell is exposed to it. This allows solar cells to generate electricity consistently during daylight hours, providing a renewable and sustainable source of power.
Overall, solar cells function at the molecular level by converting sunlight directly into electricity through the photovoltaic effect, enabling the generation of clean and renewable energy for a wide range of applications.
Thank you,